Key Takeaways:
- Preventive maintenance is a proactive approach to maintaining machinery and facilities, reducing breakdowns and unplanned downtime through early issue detection.
- There are three main types of preventive maintenance: condition-based, time-based, and usage-based, each with varying schedules and tasks depending on the asset’s condition and usage.
- Preventive maintenance offers numerous benefits, including increased efficiency, reduced downtime, prolonged equipment lifespan, and improved safety, ultimately leading to cost savings and enhanced productivity.
In This Article:
- What Is Preventive Maintenance? Definition and Importance
- What Are the Main Types of Preventive Maintenance?
- Principles and Elements of a PM Program
- What Assets Require Preventive Maintenance?
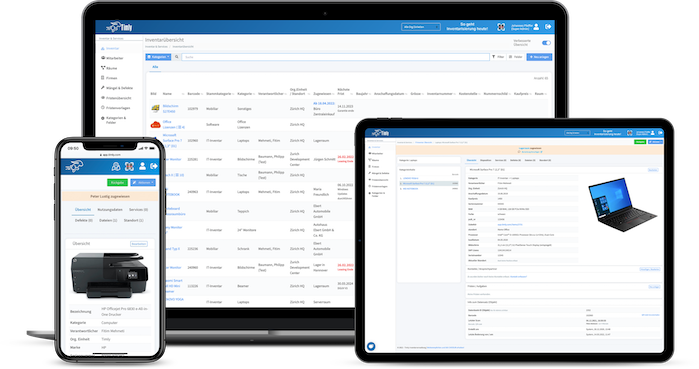
- Asset Management Software in Use by Our Customers
- How To Write A PM Maintenance Plan
- How Much Does Preventive Maintenance Cost?
- Software and Tools for Maintenance Management
- Common Preventive Maintenance Challenges
- Frequently Asked Questions About Preventive Maintenance
What Is Preventive Maintenance? Definition and Importance
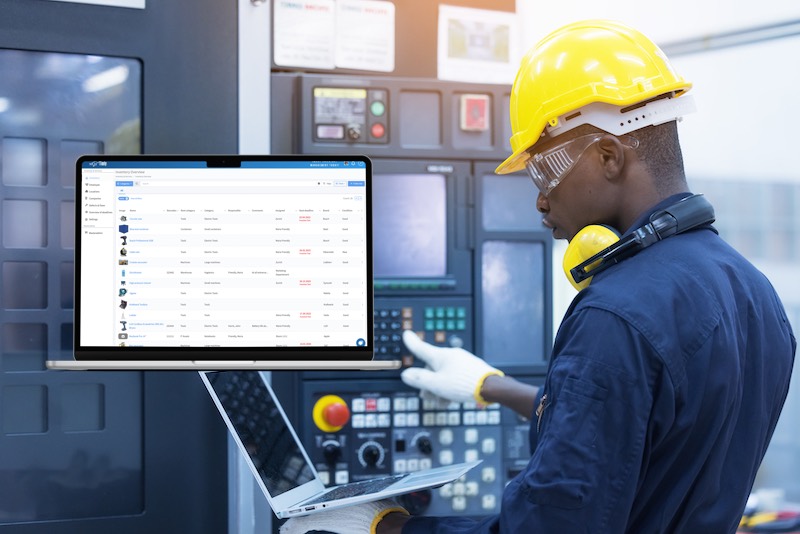
It is important to understand that preventive maintenance is essential. To fully grasp this, we need to look at its role in managing equipment and prolonging their lifespan through proactive methods to maintain machinery and facilities. Preventive maintenance helps minimize the occurrence of unwanted breakdowns and repairs. This in turn helps prevent unplanned downtime as early detection helps resolve issues before they become a serious problem.
PM is important for machinery and operations because it:
- Increases Efficiency: By performing regular maintenance, companies can ensure that their machines and equipment continue functioning at optimal levels. This saves energy and improves performance.
- Reduces Downtime: Regular maintenance helps identify and address potential issues before they become problems. This minimizes downtime, which could potentially impact revenue.
- Provide Better Safety: Regular maintenance helps identify potential risks and hazards. This helps mitigate accidental risks and provide a safer working environment.
Preventive Maintenance Meaning
There are two types of maintenance, the first is preventive maintenance on equipment, and the other is preventative maintenance.
Preventive maintenance is when equipment or assets are regularly maintained to ensure reliable performance. This involves performing maintenance checks such as cleaning, inspecting, and ensuring lubricating equipment and machinery to prevent failures and the risk of downtime. This type of maintenance typically occurs after the equipment has been in operation for around 100 hours or within 6 months, whichever comes first.
However, preventative maintenance focuses on determining what issues the equipment and machinery may face, thereby forecasting potential issues that may arise. This is because every piece of machinery operates differently and has its own operating conditions. Predictive maintenance considers these factors to anticipate and address potential failures.
What Are the Main Types of Preventive Maintenance?
There are three types of preventive maintenance (PM), which are condition-based, time-based, and usage-based. Let’s see how each of these maintenance strategies varies in terms of schedule and tasks.
- Condition-based preventive maintenance: This is when the actual condition of the equipment warrants maintenance. It is beneficial to know asset management strategies where assets are known to experience wear over time.
- Time-based predictive maintenance: Performed at fixed intervals regardless of assets current condition. For example, maintenance may be scheduled after 10,000 hours of operational service or every six months.
- Usage-based predictive maintenance: This maintenance is tied to the number of hours or the duration the asset has been used.It involves calculating and determining, based on the asset’s performance, when the equipment has reached its operational threshold.
Over 600 Companies, Schools and Cities Rely on Timly
(No credit card required)
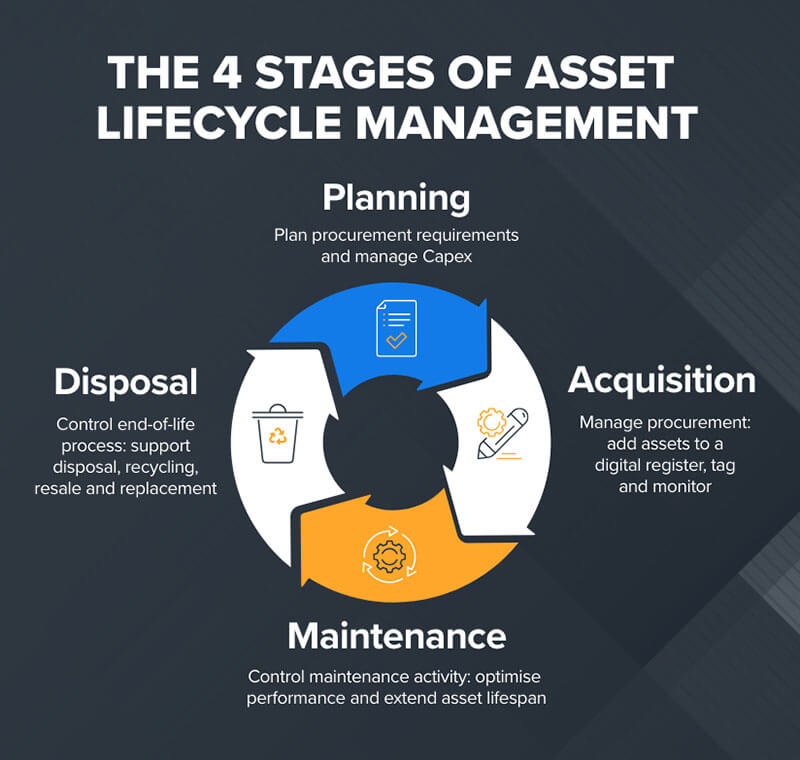
Principles and Elements of a PM Program
To understand the principles and elements of a preventive maintenance program, let us look at the key components that work cohesively to achieve these goals. They are:
- Predictive maintenance focuses on using data and sensors to monitor the performance of equipment to predict when it’s time to schedule maintenance. This is a proactive method rather than a reactive method.
- Total productive maintenance involves everyone, from stakeholders to maintenance managers to technicians. It ensures a collaborative approach to proper equipment upkeep.
- Condition-based maintenance is an approach in which equipment is monitored and maintenance is conducted based on the equipment condition.
- Scheduled maintenance is a preventative measure that ensures equipment is properly maintained. The maintenance is based on a predetermined schedule.
As for the principles of maintenance, the following are measures that need to be taken into consideration:
- Total buy-in: When implementing preventive maintenance, it is essential to obtain buy-in from stakeholders. Furthermore, it is essential to identify and discuss goals, skill sets, and resources with each team.
- Equipment history: Maintaining records of equipment history in terms of maintenance and performance is important. This allows one to identify trends, analyze metrics, and schedule preventive maintenance to optimize the asset management lifecycle phases of the equipment.
- Reliability engineering: By utilizing state-of-the art analysis and data mining, one can learn and identify the root causes of system failures and develop solutions to address them.
- Maintenance planning: This is important to ensure proper prevention strategies are in place such as scheduling, prioritizing, and allocating resources.
- Training and education: All staff must be provided the necessary training and education to understand the importance of maintenance management software.

What Assets Require Preventive Maintenance?
It is important that preventive maintenance is conducted on various assets and equipment to ensure they function properly. Here are some examples of assets that would benefit from preventive maintenance:
- Machines and Equipment: In industry, assets such as pumps, compressors, and generators require regular maintenance. This helps to ensure smooth operations and reduce any unwanted breakdown.
- HVAC Systems: Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems require regular maintenance to maintain air quality, conserve energy, and reduce repair costs.
- Automotive Vehicles: Cars, trucks, and other types of vehicles require regular maintenance to ensure safe operation, extend lifespan, and minimize breakdowns.
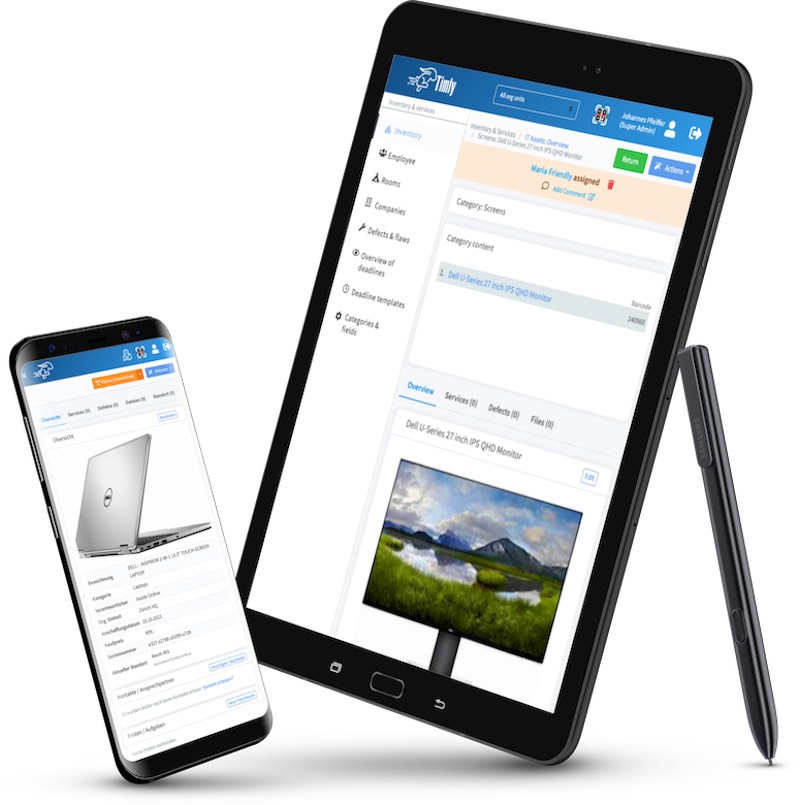
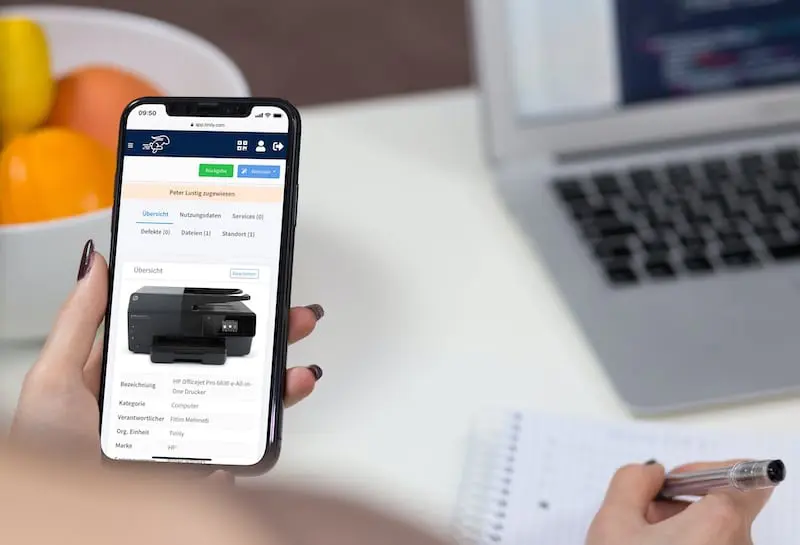
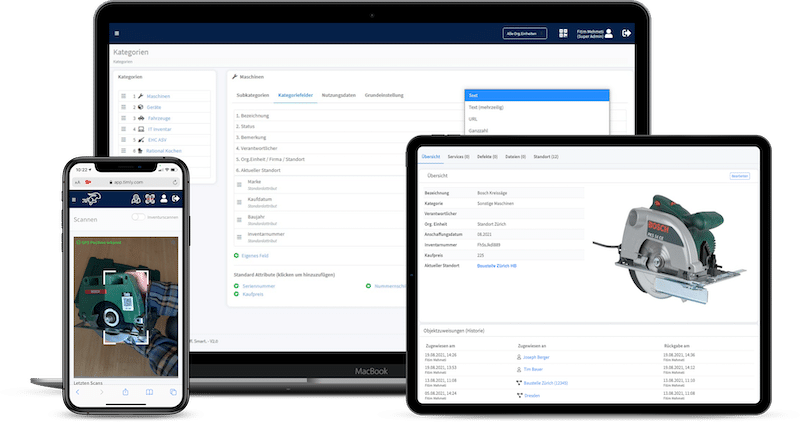
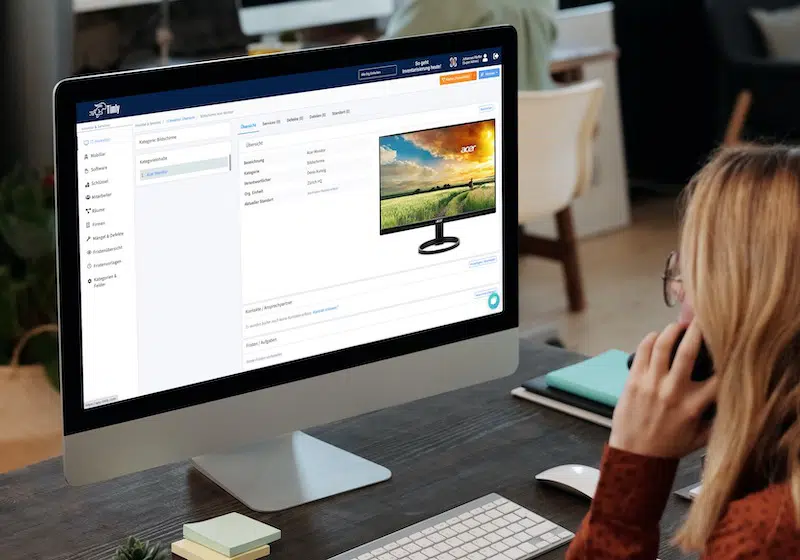
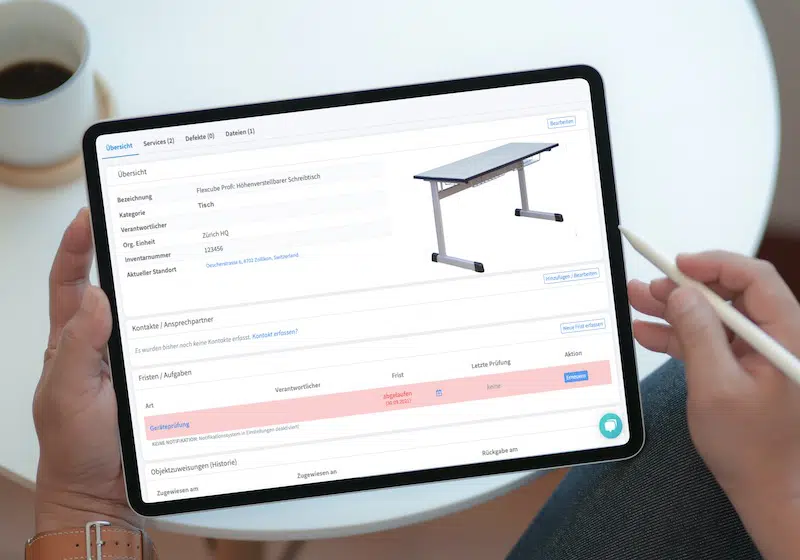
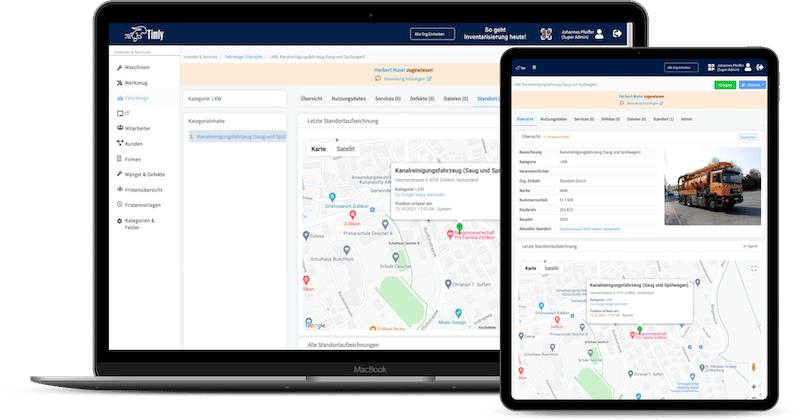
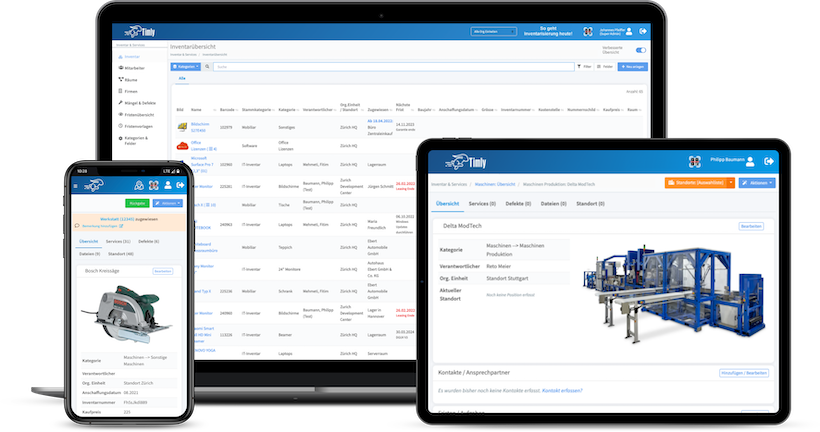
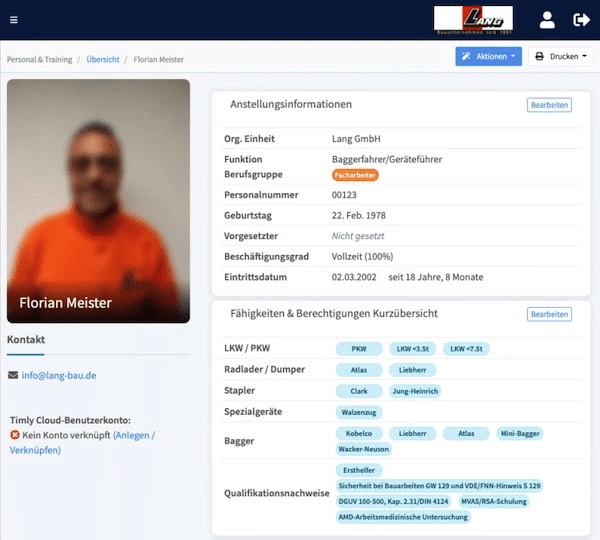
Asset Management Software in Use by Our Customers
The Timly software is continuously evolving to meet the needs of our customers. In various success stories, we show you how Timly optimizes processes in companies, thereby saving significant effort. With Timly, inventory management becomes child’s play.

Optimized Device Management With Innovative Self-Inventory
SodaStream is the world market leader for water sparkling systems for domestic use and has a lot of IT equipment at its various locations. Many colleagues now work from their home offices. A digital solution for the efficient management of IT end devices became necessary...

Panasonic x Timly: Driving Technological Innovation
One of the most remarkable aspects of human ingenuity is our ability to innovate. Innovation is embedded in the DNA of consumer electronics giant Panasonic, which has diversified into a number of sectors, from heavy industry to construction...

Manage Video Equipment Efficiently Without Much Effort
The Hamburg media company always does outstanding journalistic work and is characterized by independent reporting. In order to maintain journalistic quality, the teams work with highly specialized devices – these need to be managed efficiently...

Smart City Asset Management – Timly in Use at DIGOOH
The core business of DIGOOH Media GmbH in Cologne is to manage digital city light posters (DCLP) for outdoor use in various cities in Germany. The challenge here lies in making the client’s communication message always available at the right time, in the right place...
(No credit card required)
How To Write A PM Maintenance Plan
If you are interested in writing a preventive maintenance plan, then you can begin by identifying the necessary goals and objectives. This will help you identify what tasks need to be added to the plan. Here are a few steps:
- Start by defining the scope.
- Determine frequency of maintenance.
- Find out who or which department will be responsible for performing these tasks.
- Create a schedule that will outline each and specify how it is performed.
- Finally, ensure that the plan is regularly monitored and reviewed.
How to Create a Preventive Management Checklist
In order to create a preventive management checklist, follow these steps:
- Gather information regarding which equipment, machinery, or assets need to be scheduled for maintenance. Ensure that the information collected includes details about their usage, operating conditions, and recommendations from the manufacturer.
- Set goals for desired outcomes you would like to see from the preventive maintenance program. Make sure these goals are aligned with the company’s objectives.
- Assign specific maintenance responsibilities to team members or technicians who are familiar with the equipment and operations.
- Create a template or spreadsheet to organize your checklist. The columns should include information such as equipment name, maintenance tasks, maintenance frequency, due date, team or personnel responsible, and any relevant comments. You could use a digitized checklist, like a maintenance management system, to streamline the information and make it easily accessible to teams.
How Much Does Preventive Maintenance Cost?
The costs of preventive maintenance depend on the type of equipment, industry, and the frequency of maintenance. Here’s a general understanding of how much preventive maintenance costs for certain equipment within their respective industry.
The average median tied to maintenance could range from USD 211 to USD 222 billion. This is due to preventive maintenance lowering unplanned downtime by 48.5% and provides significant cost savings.
Some industries estimate that predictive maintenance can provide savings of USD 200 million to USD 600 billion in manufacturing.
Though the exact cost of preventive maintenance can vary depending on the industry, it is understood that it can provide significant cost saving benefits, reduce downtime, and increase productivity.
How Often Should Preventive Maintenance Be Performed?
Preventive maintenance should be performed by considering several factors, including usage, age, and type of equipment. If we are dealing with heavy machinery, then it needs to be serviced more frequently than machinery that is hardly used. For example, it is often recommended to change the oil in a car every 3,000 miles, regardless of driving conditions.
Moreover, regular inspections are necessary, considering the failure developing period (FDP), which is the time between the initial failure and breakdown. For instance, if a pump starts cavitating at 6 am and breaks down at 6 pm, six 6 days later, the failure developing period would be 156 hours. The frequency of inspection would be FDP/2, resulting in 78 hours.
In addition, some equipment requires time-based preventive maintenance. This includes regular inspections and part replacements. For example, time-based preventive maintenance could involve changing air filters every 3 months. The goal is to find the balance between performing maintenance too frequently or neglecting inspections, which would lead to equipment failure.
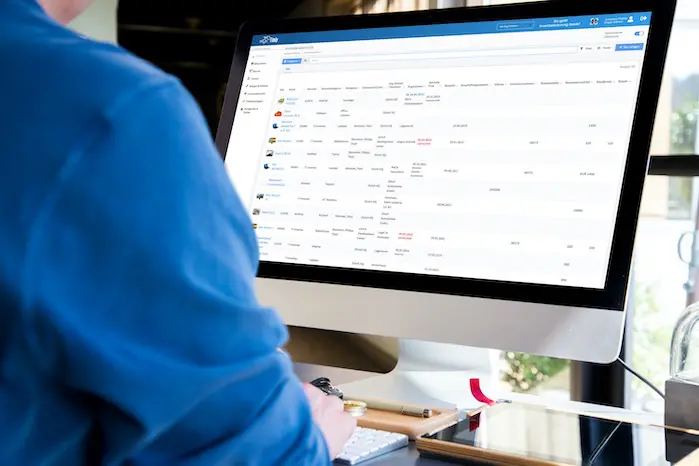
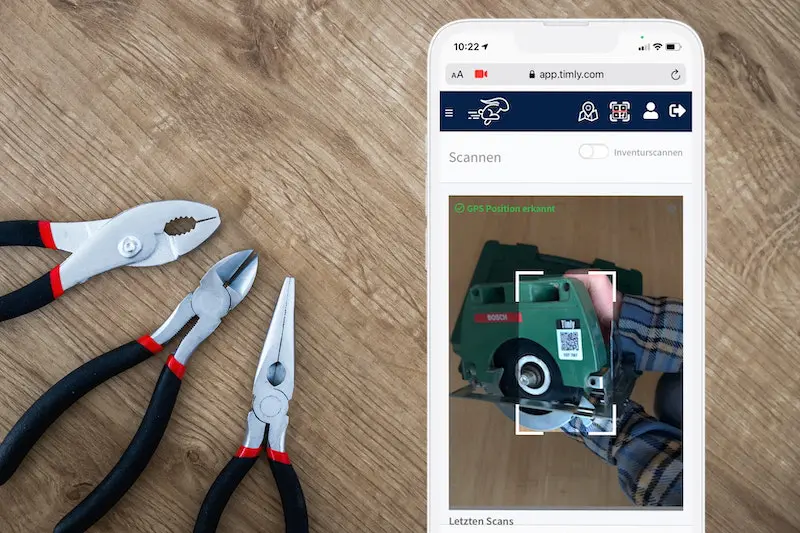
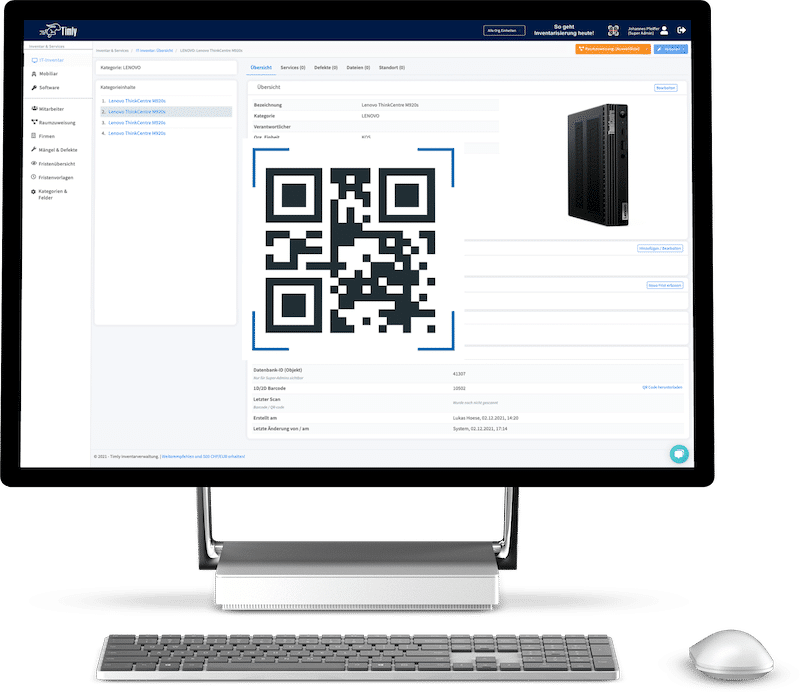
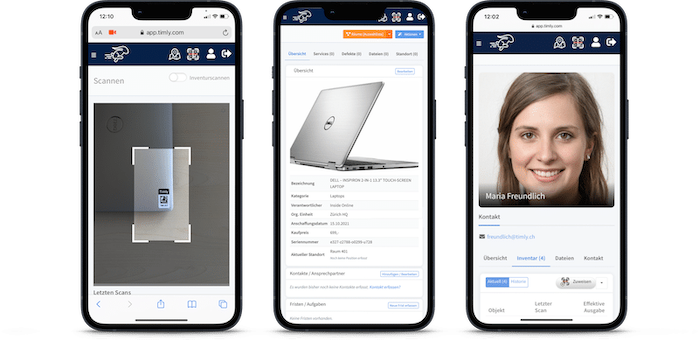
Software and Tools for Maintenance Management
When selecting software and tools for maintenance management, companies should consider options that help manage and optimize their operations.Here are some tools that could help:
- Asset Essentials: This software helps provide security and compliance planning. It provides metrics and supports EH&S documentation.
- Axxerion: This tool provides preventive, corrective, and predictive maintenance. It serves as an enterprise asset management (EAM) system, which is used to track equipment.
- Timly’s CMMS System: This cloud-solution reminds users of upcoming maintenance dates, provides easy maintenance planning, and helps track defects and performance.
Common Preventive Maintenance Challenges
- Time and Resources: This requires planning, scheduling, budgeting, and allocating personnel, which can be time-consuming.
- Balancing Maintenance With Production: As preventive maintenance often requires the shutting down or removal of equipment, it’s essential to ensure minimal disruption to production.
- Data Management: Maintaining data and information related to asset performance and maintenance can be challenging. This can pose an issue for large-scale operations.
Benefits of Preventive Maintenance
Preventive maintenance must be conducted frequently to ensure the longevity and efficiency of equipment, facilities, and systems. By implementing preventive maintenance strategies, you can realize many benefits, such as cost savings, improved productivity, and better performance. Here are some benefits of preventive maintenance:
- Asset Lifespan: Regular maintenance extends the equipment’s lifespan and reduces the need for early replacement. This helps mitigate unwanted costs.
- Equipment Reliability: Preventive maintenance ensures optimum functionality, reduces the number of breakdowns and downtime.
- Maintenance Costs: You will be able to save costs by proactively addressing issues, which reduces the number of repairs and replacements.
- Enhanced Safety: Enforcing preventive maintenance reduces the risk of accidents and injuries by identifying hazards before they become an issue.
- Increased Productivity: By having equipment that is running smoothly, companies can increase their production levels.
What Are the Limitations of PM Maintenance?
As seen, there are many benefits to preventive maintenance. It provides efficiency by reducing downtime and extending the longevity of the equipment. However, there are certain limitations to PM.
- Costs: Preventive maintenance can be quite costly. Thus, small businesses may struggle due to their limited budget. Hence, utilizing or investing in a CMMS or other known tools could be an issue due to cost.
- Resources: Businesses that are new or growing may face challenges in implementing preventive maintenance, as it requires extra staffing, spare parts, and time.
- Budget: You may need to provide an upfront payment, which can be a problem for companies with a limited budget.
- Scheduling: An inaccurate maintenance schedule lead to unwanted downtime or missed maintenance opportunities.
Frequently Asked Questions About Preventive Maintenance
What Is Preventive Maintenance?
How to Create a Preventive Management Checklist
To create a preventive maintenance checklist, follow these steps:
- Gather information regarding which equipment, machinery, or assets need to be scheduled for maintenance. Ensure that the information collected includes details about their usage, operating conditions, and recommendations from the manufacturer.
- Set goals for desired outcomes you would like to see from the preventive maintenance program. Make sure these goals are aligned with the company’s objectives.
- Assign specific maintenance responsibilities to team members or technicians who are familiar with the equipment and operations.
- Create a template or spreadsheet to organize your checklist. The columns should include information such as equipment name, maintenance tasks, maintenance frequency, due date, team or personnel responsible, and any relevant comments.. You could use a digitized checklist, like a maintenance management system, to streamline the information the information and make it easily accessible to teams.
Recommended for You:
Book an online demo - free and without obligation - or create your free trial account directly.