Key Takeaways:
- Equipment depreciation life refers to the period over which equipment is expected to lose its value.
- The useful life of an item refers to how long an equipment can be used or remain productive before becoming obsolete.
- When considering production methods for manufacturing machinery depreciation, organizations must account for machinery costs based on usage and productivity.
- To decide whether to depreciate or expense equipment, consider factors such as your investment size, expenditure rate, and tax implications for the organization.
In This Article:
- What Is the Equipment Depreciation Life and Its Significance?
- How Do You Calculate and Determine the Useful Life of Equipment?
- What Factors Impact the Equipment’s Useful Life?
- Best Practices for Extending the Useful Life of Equipment and Machinery
- Asset Management Software in Use by Our Customers
- Expensing vs. Depreciating Equipment
- What Assets Are Depreciated Over 7 Years?
- What Equipment Is Depreciated for 5 Years?
- Frequently Asked Questions About Equipment Depreciation Life
What Is the Equipment Depreciation Life and Its Significance?
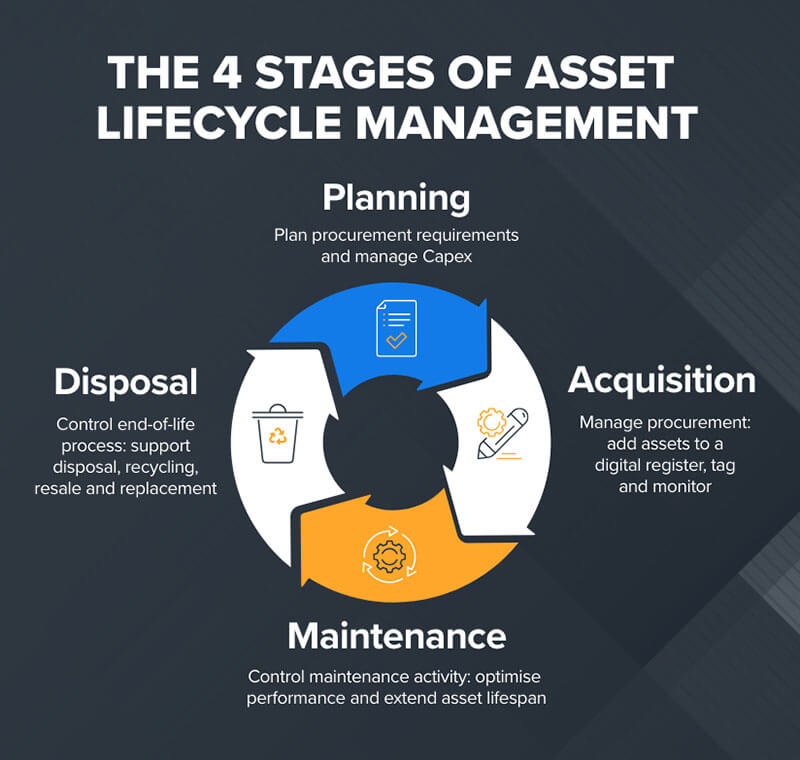
Equipment depreciation life refers to the period over which equipment is expected to lose its value. This depreciation can occur due to factors such as wear and tear, obsolescence, and other related factors. Understanding equipment depreciation life is essential for annual tax reporting and fiscal planning. Additionally, it plays a crucial role in organizational decision-making processes, helping to determine the optimal time for asset replacement or acquisition of new equipment. By accurately identifying the rate of equipment depreciation, organizations can make informed decisions to optimize revenue, foster growth, and minimize downtime associated with equipment depreciation.
What Is the Useful Life of Equipment?
The useful life of an item refers to how long an equipment can be used or remain productive before becoming obsolete. Let’s explore the lifespans of various types of equipment:
- Office equipment, such as printers and laptops, typically has a lifespan of about 3-5 years.
- Depending on maintenance and usage, manufacturing equipment like heavy machinery can last anywhere from 10 to 30 years.
- Construction equipment, such as cranes or bulldozers, generally has a life expectancy of 10-20 years.
- Medical equipment’s lifespan varies based on technological advancements and the type of equipment, ranging from just a few years to several decades.
Several factors influence equipment life expectancy. Firstly, maintenance is essential, requiring constant attention, including preventive and corrective maintenance, to prevent breakdowns. Additionally, usage patterns play a significant role; equipment subjected to heavy loads may have a shorter lifespan than those used for lighter tasks. Moreover, technological advancement impacts equipment longevity, as outdated technology may render equipment obsolete sooner. Therefore, it’s important to ensure that the tools used remain relevant in the face of rapid technological evolution.
What Is Standard Depreciation for Equipment?
An equipment’s standard depreciation relies on its cost over its lifespan, which encompasses asset depreciation, or the wear and tear of the product. Hence, organizations focus on asset depreciation to ascertain the overall cost of the equipment throughout its lifespan.
When considering depreciation rates for different types of equipment, they may vary based on the tax regulations and accounting standards that businesses adhere to. That said, two methods can be employed to assess the depreciative value of the equipment.
- Straight-line Depreciation: This method centers on the initial price of the product and its value at the end of its life (salvage value). Both values are taken into account and compared with the equipment’s useful lifespan. Therefore, it is the cost of equipment minus salvage value divided by the useful lifespan.
- Accelerated Depreciation: This method compares the equipment’s useful life in the current year with that of previous years. It assumes that the equipment’s useful life in earlier years should be shorter compared to the current year. However, if this is not the case, organizations need to analyze what went wrong and why.
What Is the Useful Life of Heavy Equipment and Machinery?
There are several factors to consider when determining the useful life of heavy equipment. These factors include the rate at which the equipment is used, the frequency of maintenance, and even technological aspects related to equipment utilization. Additionally, heavy machinery is typically designed to last a long time due to the nature of its functionality. The useful life of heavy machinery can range from 10 to 30 years. However, it is essential to consider the operating condition and the quality of the equipment in order to accurately determine its useful life.
What Is the Useful Life of Manufacturing Equipment?
Manufacturing equipment, much like heavy machinery, has its useful life determined by similar factors such as equipment usage, industry standards, maintenance frequency, and technological features. Additionally, manufacturing machinery is designed for longevity due to the demands of its tasks. For equipment like machinery tools and industrial robots, the useful lifespan typically ranges from 10 to 20 years. However, this duration is subject to various factors including quality, condition, and the implementation of product upgrades and repairs. By consistently updating and monitoring this equipment, organizations can gather insights into its performance improvement and ensure its efficiency until the end of its life or its disposal as scrap.
How Do You Calculate and Determine the Useful Life of Equipment?
To calculate and determine the useful life of equipment, organizations need to consider various factors and common standards such as the equipment’s operational requirements, technological features, maintenance frequency, and established guidelines aimed at ensuring equipment longevity. This is crucial because organizations aim to maximize equipment usage for productivity and utilize this information when generating fiscal reports and filing taxes.
To determine the useful life of equipment, you need to consider:
- Equipment Information: This requires detailed information about the equipment, including its year of manufacture, type, usage, and maintenance history.
- Manufacturer Guidelines: Understanding the guidelines provided by the manufacturer is crucial for increasing equipment lifespan.
- Industry Standards: Knowing how similar equipment operates and utilizing research and publication tools can provide insights on enhancing equipment lifespan and improving organizational best practices.
- Maintenance Standards: Consideration of maintenance frequency, whether standard, preventive, or corrective, is essential. Scheduled maintenance helps prolong the equipment’s value expectancy.
- Technological Features: Checking the equipment’s technological features is important as obsolete technology can render the equipment obsolete at a young age, impacting the company’s revenue.
- Operating Conditions: Understanding the conditions under which the equipment will operate, including its environment, usage, and exposure to corrosion, is imperative for calculating its useful life.
- Selected Calculations: Depreciation rates vary based on equipment type, industry standards, regulations, and technological advancements. Accurately calculating depreciation and useful life impacts budgeting, costing, and tax filing.
- Budget and Costing: Accuracy in forecasting yearly budget and expenses helps optimize resource allocation.
- Tax Filing: Compliance with tax regulations is crucial for tax purposes and financial planning.
By carefully considering these factors, utilizing appropriate depreciation methods, and accurately calculating the useful life of equipment, businesses can make informed decisions, optimize financial planning, and effectively manage their assets. By using Timly’s asset management software, you will be able to identify your machine’s usage and optimization and gain insights into its potential. From here, you can identify your equipment’s depreciation and plan ahead.
Units of Production Method for Manufacturing Machinery Depreciation
When considering production methods for manufacturing machinery depreciation, organizations must account for machinery costs based on usage and productivity. While it might seem appropriate to apply a gradual depreciation rate, it may not accurately reflect the actual production rate or hours the machine has been utilized to generate output. Let’s delve into how this is accomplished.
- Calculation: To determine an item’s depreciation rate over time, multiply the unit cost by the number of hours the machine was in use, then divide by the total operational hours of the equipment’s useful life.
- Flexibility: To obtain accurate depreciation values, it’s crucial to employ the unit of production method. This method focuses on the actual output that the machine has generated, making it suitable for machinery with varying levels of usage or production.
This method finds application in various industries, including:
- Manufacturing: Suitable for reflecting the wear and tear of equipment such as presses and stamping machines.
- Mining: Since it is tied closely to resource-generating activities like drilling for oil and mining, it aligns well with equipment usage and output.
- Agriculture: In farming, equipment such as tractors and irrigation systems sees usage directly impacting output, making the unit of production or hours used critical factors.
Therefore, the unit of production method provides a more accurate valuation, particularly in industries reliant on equipment production rates. Organizations require this accuracy for providing stakeholders and investors with precise reporting and aligning with future cost management.
Over 600 Companies, Schools and Cities Rely on Timly
(No credit card required)
What Factors Impact the Equipment’s Useful Life?
We know that factors such as equipment usage, maintenance practices, and even technological features impact the useful life of equipment. So, how do these factors affect different assets? Let’s examine an example for a clearer understanding.
Case study: Consider two tractors used in agricultural fields. Tractor A is utilized for heavy loads, while Tractor B handles lighter loads. It’s evident that Tractor A will experience faster wear and tear compared to Tractor B. This difference arises from several factors, including the environment each tractor is exposed to, the technological features they possess (whether similar or different), and the maintenance practices applied to each tractor.
Best Practices for Extending the Useful Life of Equipment and Machinery
When considering best practices to enhance the useful life of equipment and machinery, it’s essential to factor in the maintenance rate: whether inspections are conducted regularly, preventive maintenance measures are in place, and repairs are promptly addressed. Additionally, personnel should be trained to handle and operate machinery efficiently, enabling them to identify issues before they escalate. Machinery with advanced technological features requires continuous monitoring and management to ensure optimal performance. Without proper upgrades and bug fixes, constant breakdowns can hinder operational efficiency. Environmental and sustainable factors should also be considered, as they play a crucial role in determining the equipment’s lifespan while reducing breakdowns and increasing operational output.
What Is the 50% Rule in Depreciation?
Organizations utilize this method to ensure compliance with financial regulations, accurately reflect financial records, and ensure that the equipment’s rate of improvement or depreciation is correctly reflected in fiscal reports.
Asset Management Software in Use by Our Customers
The Timly software is continuously evolving to meet the needs of our customers. In various success stories, we show you how Timly optimizes processes in companies, thereby saving significant effort. With Timly, inventory management becomes child’s play.

Optimized Device Management With Innovative Self-Inventory
SodaStream is the world market leader for water sparkling systems for domestic use and has a lot of IT equipment at its various locations. Many colleagues now work from their home offices. A digital solution for the efficient management of IT end devices became necessary...

Panasonic x Timly: Driving Technological Innovation
One of the most remarkable aspects of human ingenuity is our ability to innovate. Innovation is embedded in the DNA of consumer electronics giant Panasonic, which has diversified into a number of sectors, from heavy industry to construction...

Manage Video Equipment Efficiently Without Much Effort
The Hamburg media company always does outstanding journalistic work and is characterized by independent reporting. In order to maintain journalistic quality, the teams work with highly specialized devices – these need to be managed efficiently...

Smart City Asset Management – Timly in Use at DIGOOH
The core business of DIGOOH Media GmbH in Cologne is to manage digital city light posters (DCLP) for outdoor use in various cities in Germany. The challenge here lies in making the client’s communication message always available at the right time, in the right place...
(No credit card required)
Expensing vs. Depreciating Equipment
The difference between expensing and depreciating equipment is as follows:
- Expensing: This method involves treating equipment as a business cost at the time of its purchase. The entire cost is immediately deducted, and the deduction is calculated to reflect the income tax bracket for the year.
- Depreciating: With this method, the wear and tear of the equipment is factored in over the number of years it is utilized. In other words, the cost of the equipment is spread out over its useful life.
Expensing is suitable for shorter expenses, while depreciating is more appropriate for larger and longer-term investments. This distinction is utilized to ensure lasting usage for the business and impacts tax deductions and filing.
Do I Have to Depreciate Equipment or Can I Expense It?
To decide whether to depreciate or expense equipment, consider factors such as your investment size, expenditure rate, and tax implications for the organization. For example, if the expenditure is primarily for minor repairs or maintenance costs, it falls under expenses. However, if the expenses provide long-term benefits, then it falls under depreciation.
Regarding tax implications, expensing an item reduces taxable income for the year, resulting in lower tax liabilities and better tax deduction rates for companies. On the other hand, depreciation spreads out the deduction over the years, providing tax benefits gradually. Understanding this criteria is important because it helps organizations make informed decisions when investing in equipment.
What Assets Are Depreciated Over 7 Years?
Assets that depreciate over seven years include:
- Computer Equipment: This includes chairs, filing cabinets, and desks.
- Office Equipment: This includes printers, scanners, and other office machinery.
- Heavy Machinery: This includes bulldozers, tractors, and other machinery.
This is considered accelerated depreciation when filing taxes because it depreciates over a period of seven years. This is why asset management matters and organizations use this method to deduct a significant amount from their costs to save on taxes. Additionally, it places them in a lower tax bracket because depreciation expenses are spread over the seven-year period. This allows businesses to strategically plan their asset investments, optimize tax savings, and ensure compliance with tax regulations.
What Equipment Is Depreciated for 5 Years?
Equipment that depreciates over a timeframe of five years includes:
- Furniture: Chairs, filing cabinets, sofas, etc.
- Medical Equipment: Items such as diagnostic machines and imaging equipment.
- Furniture and Fixtures: Office furniture, including desks, chairs, tables, and filing cabinets, is commonly depreciated over a 5-year period.
Frequently Asked Questions About Equipment Depreciation Life
What Is the Equipment Depreciation Life and Its Significance?
What Is the Useful Life of Heavy Equipment and Machinery?
Recommended for You:
Book an online demo - free and without obligation - or create your free trial account directly.