- The depreciation life of medical equipment influences financial planning, tax reporting, and equipment longevity.
- Understanding the depreciation life is crucial for calculating expenses, allocating resources, and determining equipment replacement.
- The depreciation rate affects the equipment type, helpful life, and accounting method.
- Depreciation Life of Medical Equipment
- How Is the Useful Life of Medical Equipment Determined?
- What Are the Depreciation Rules and Methods for Medical Equipment
- How Is Depreciation of Medical Equipment Calculated?
- Why Is It Important to Calculate Equipment Depreciation?
- What Is an Equipment Depreciation Schedule?
- How Do Depreciation Policies Impact Medical Practices?
- How Long Should Medical Equipment Last?
- Frequently Asked Questions About the Depreciation Life of Medical Equipment
Depreciation Life of Medical Equipment
Medical equipment depreciation life is the time it takes to depreciate medical equipment or appliances. This is the loss of equipment value due to wear and tear, technological obsolescence, and other factors. It is the period of depreciation, and thus, expenses for tax and financial reporting purposes must be calculated.
It is crucial to understand depreciation life so that it helps:
- Healthcare administrators calculate expenses, allocate resources, and know when it is time for equipment replacement and upgrade.
- Calculate tax to determine the depreciation of assets annually. This helps to reduce taxable income and tax liabilities.
- Determine effective management strategies for maintenance, repair, and replacement of equipment.
- Ensure that budgeting and costs are controlled, thus allowing for advanced accounts and predictability.
Here is an overview of depreciation’s impact on financial planning and tax reporting:
- Medical equipment depreciates using a straight-line method. The cost of the asset is spread evenly over time.
- Depreciation rates differ according to the equipment type, helpful life, and the accounting method used.
- Bonus depreciation may be available to claim a significant deduction rate in the asset’s early years.
- Deduction for healthcare providers to use a certain amount for medical equipment in the first year.
How Is the Useful Life of Medical Equipment Determined?
A few factors, such as specifications, usage, and industry standards, define the useful life of medical equipment. For instance, manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations are essential to determining the lifespan of medical equipment. The frequency and intensity of using the equipment can impact lifespan. Industry standards set by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) aid in the service life of medical equipment, such as:
- Regular maintenance would extend the lifespan of the equipment.
- The rate of technological devices in the medical field can cause equipment to be obsolete.
- The medical equipment has a lifespan because its usage is safe and meets its performance specifications. The manufacturer defines the expected service life, which can be extended through potential refurbishment.
What Is the Effective Life of Medical Equipment?
The practical life of medical equipment is the time an asset takes to generate or produce a desired income under the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). It is different from the physical lifespan, which concerns the usage period of the equipment, including the operational hours until it becomes obsolete or reaches end-of-life. Thus, there is a difference between physical lifespan and effective lifespan.
Understanding the effective lifespan of medical equipment is essential to understanding the rate of depression. This would ensure that the asset remains useful for tax purposes, and its increasing value over time would also allow businesses to claim depreciation deductions on their tax returns.
Let us look at some examples of types of medical equipment and the difference in their lifespan:
- Diagnostic machines such as MRIs, CT scans, and ultrasound machines would last around 5 to 7 years.
- Imaging equipment such as X-rays, mammography, and PET scans lasts 7 to 10 years.
- Surgical equipment such as lasers, electrosurgical units, and orthopedic implants may last around 10 to 15 years.
- Furniture such as hospital beds, stretchers, and medical carts lasts 5 to 10 years.
- Other equipment, such as ventilators, dialysis machines, and infusion pumps, may last around 10 to 20 years.
What Are the Depreciation Rules and Methods for Medical Equipment
The depreciation rule is a medical practice that focuses on recovering the cost of medical equipment. The depreciation method depends on factors such as equipment type, helpful life, and the tax situation of the practice. This includes:
- The straight-line method. It focuses on deducting the cost of the equipment over its lifespan. For instance, if the medical equipment costs around USD 10,000 and has a lifespan of 5 years, the depreciation rate would be USD 2000 a year.
- The double declining balance method focuses on deducting in the early years of a valuable life. It is twice the straight-line rate, which can be switched to the straight-line method for better revenue.
- The modified accelerated cost recovery system (MACRS) method. It calculates the annual depreciation rate using a set of predetermined periods and rates. This method is commonly used for depreciation in most businesses.
The guidelines for medical equipment include:
- Medical practices that deduce up to USD 1,160,000 of the cost of specific equipment in the year of its initial service.
- Special depreciation allowance allows medical practitioners to deduct the additional equipment costs in the year of its service.
The choice of depreciation method depends on the following factors:
- The type of equipment used.
- The longer the equipment’s lifespan, the more beneficial the straight-line method.
- Medical practices with high tax incomes may benefit from the double declining balance or MACRS method.
- Medical practices have specific cash flow limits, which may benefit them from using the straight-line method to spread expenses over a more extended period.
What Is the Depreciation Rate for Medical Equipment?
- The straight-line method uses a 5-year depreciation period. Each year would cost a depreciation of 20% or 1/5th of the asset costs. For instance, if a machine costs around USD 100,000, the depreciation rate would be USD 20,000.
- The modified accelerated cost recovery system (MACRS) is used for tax purposes and allows for accelerated depreciation in the early years of the equipment. For instance, equipment that costs USD 500,000 would depreciate as follows:
- 20% during the first year, which is USD 100,000.
- 32% during the second year, which is USD 160,000.
- 19.2% during the third year, which is USD 96,000.
- And the depreciation rate continues.
The depreciation rate affects:
- The income statement. It reduces net income and affects the company’s profit rate. Depreciation also affects the balance sheet.
- Tax deductions. They are updated with tax-deductible income, resulting in lower tax liabilities. The straight-line, or MACRS, depreciation method determines the impact and amount of tax deductions.
Depreciation rates are different depending on the type of industry and medical equipment. They are:
- Imaging equipment such as MRI and CT scanners depreciates in 5 to 7 years, with a higher depreciation rate in the early years.
- Surgical equipment, such as laparoscopic instruments, depreciates within 5 to 10 years. Due to their longer lifespans, they have a more gradual depreciation rate.
- Diagnostic equipment. It has a depreciation period of 5 to 7 years.
- Hospital equipment such as ventilators and dialysis machines. It has a depreciation rate of 10 to 15 years.
How Is Depreciation of Medical Equipment Calculated?
Here are a few depreciation methods:
- Straight-line depreciation focuses on the equal rate of decline in value over the asset’s useful life. For instance, the rate of depreciation = (cost – salvage value)/useful life. If a hospital bought an MRI machine for around USD 1 million with a salvage value of USD 100.000 and a useful life of 10 years, the annual depreciation would be:
- Deprivation = (USD 1,000,000 – USD 100,000)/10 = USD 90,000 a year.
- A modified accelerated cost recovery system (MACRS) accelerates the depreciation rate in the early years. For instance, the formula is depreciation = (cost – salvage value) x depreciation rate. Thus, if a clinic purchases a CT scanning machine for USD 800,000 with a salvage value of USD 80,000 with a useful life of 5 years, then annual depreciation would be:
- Year 1 depreciation = USD 800,000 x 20% = USD 160,000
- Year 2 depreciation = USD 800,000 x 32% = USD 256,000.
- Units of production depreciation is a calculation method based on equipment usage. Thus, the formula is depreciation = (cost – salvage value) x (total units produced/total units expected). So, if a dental practice purchases units of USD 50,000 with a salvage value of USD 5,000, the expected price is USD 10,000 for 5 years. After 2 years, the unit produced is 4,000, giving an annual depreciation of:
- Depreciation is calculated as USD 9,500/year, equal to (USD 50,000 – USD 5,000) x (4,000 / 20,000).
Tools and worksheets that can be used to simplify depreciation calculations are:
- Online calculators such as Nerdwallet’s Depreciation.
- Spreadsheets such as a depreciation calculator template.
- Worksheets can be created using tables with columns for depreciation methods and annual depreciation amounts.
Best Depreciation Method for Hospitals
The best depreciation method for hospitals depends on the asset type, usage, and accounting requirements. Let us look at the pros and cons of different types of depreciation methods and the factors that influence the selection method:
- The straight-line method evens out depreciation over the useful life. This method has the pros of being easy to calculate and implement, consistent asset maintenance, and compliance with GAAP. The cons are that it does not consider the difference in usage and condition and does not reflect the declining value.
- The declining balance method accelerates depreciation by a fixed percentage. This method has the pros of reflecting usage and providing a more realistic understanding of the decline rate. However, it is difficult to calculate and may not decline with GAAP for certain assets.
- The units of production method depreciate according to its usage. The pros are that it reflects the usage of asset conditions and can be used for assets with different usage patterns. The cons of this method are that it needs detailed usage tracking and is difficult to calculate.
- The sum of years digits method is used for assets that depreciate according to the balance of years it has for its useful life. The pros are that it encourages asset replacement and maintenance and can be used for assets with different useful lives. The cons are that it does not factor in the usage and condition and may not reflect the declining value.
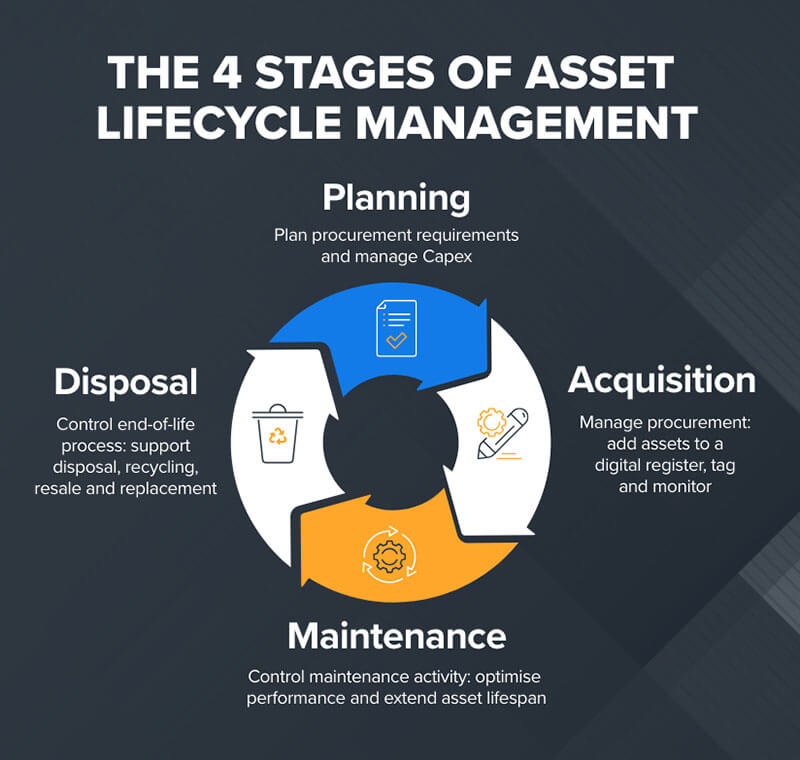
The factors influencing method selection include asset type, usage patterns, accounting requirements, and tax implications. Moreover, the recommendation for optimizing depreciation strategies in hospitals is to:
- Ensure regular tracking of asset inventory management in supply chain.
- Automate asset tracking, maintenance, and depreciation.
- Inspect and track asset usage.
- Ensure GAAP compliance and industry guidelines.
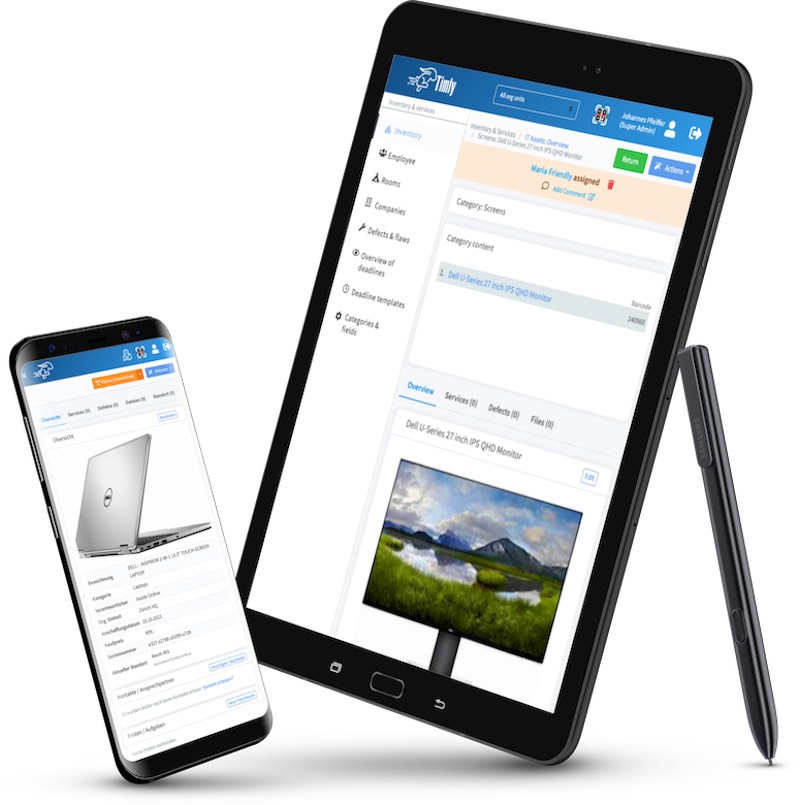
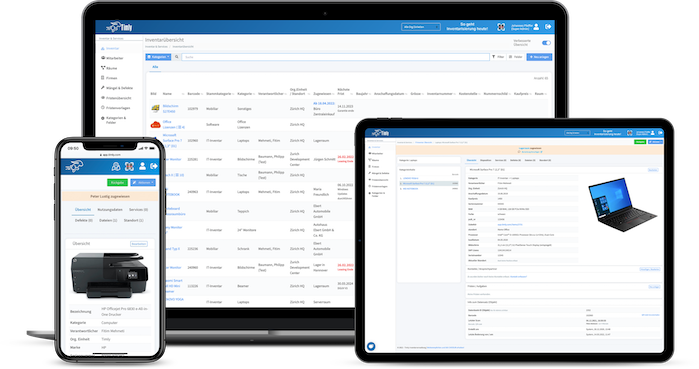
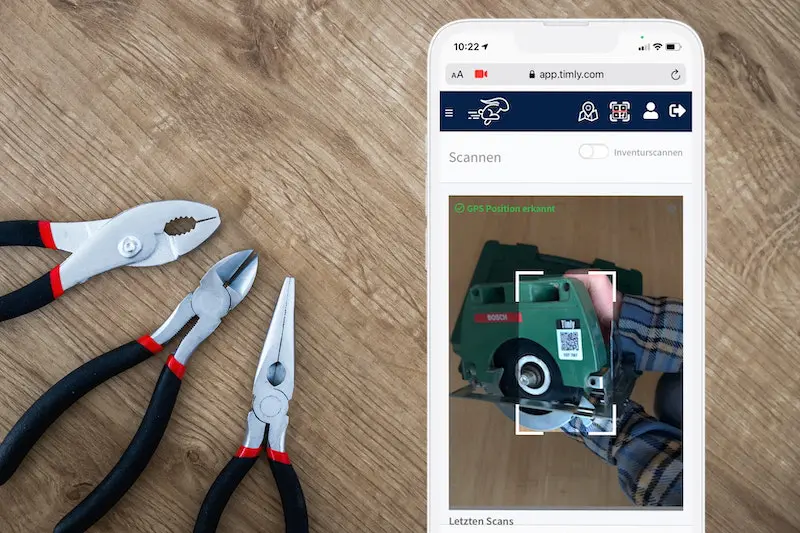
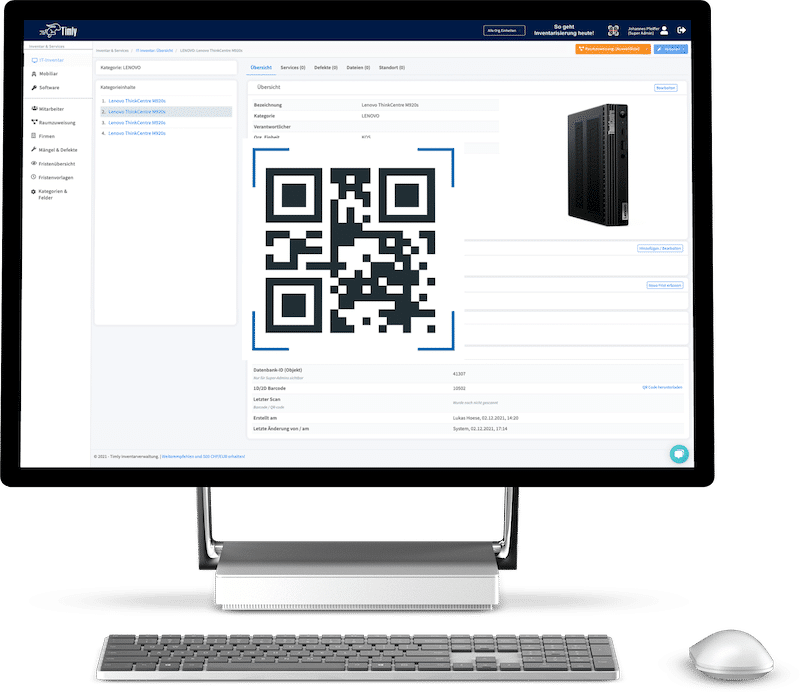
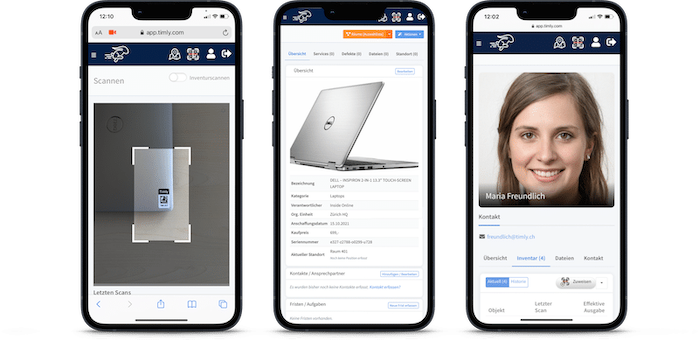
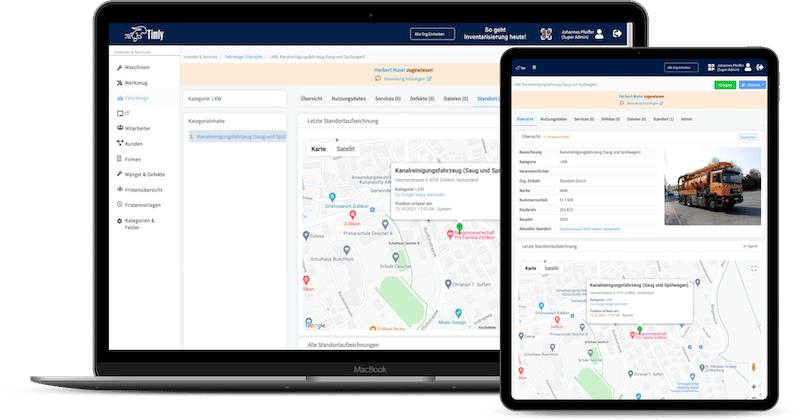
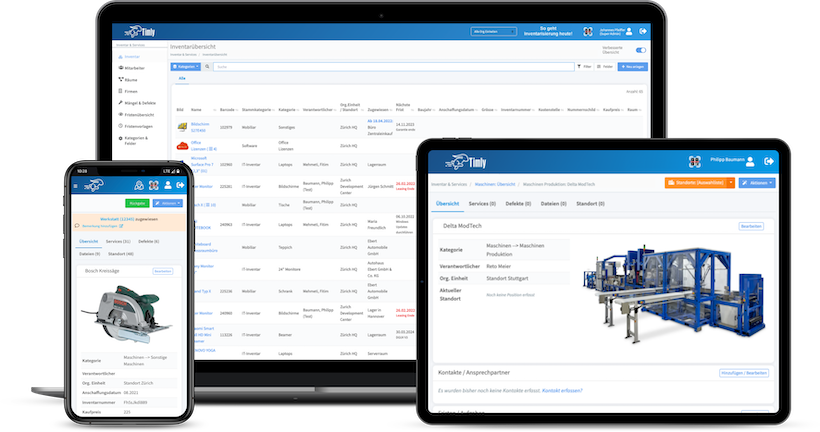
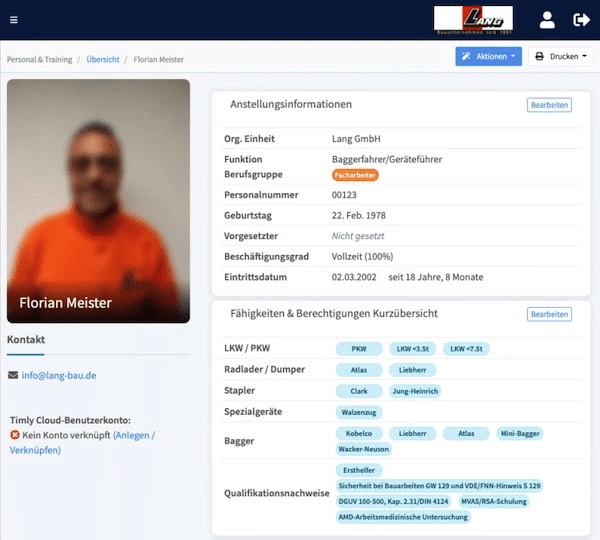
TImly’s medical device management software allows organizations to track inventory, integrate barcode inventory system, maintain records of devices, track employee usage, and generate reports and analytics for data-driven decisions.
The Timly Software in Use

Optimized Device Management With Innovative Self-Inventory
SodaStream is the world market leader for water sparkling systems for domestic use and has a lot of IT equipment at its various locations. Many colleagues now work from their home offices. A digital solution for the efficient management of IT end devices became necessary...

Panasonic x Timly: Driving Technological Innovation
One of the most remarkable aspects of human ingenuity is our ability to innovate. Innovation is embedded in the DNA of consumer electronics giant Panasonic, which has diversified into a number of sectors, from heavy industry to construction...

Manage Video Equipment Efficiently Without Much Effort
The Hamburg media company always does outstanding journalistic work and is characterized by independent reporting. In order to maintain journalistic quality, the teams work with highly specialized devices – these need to be managed efficiently...

Smart City Asset Management – Timly in Use at DIGOOH
The core business of DIGOOH Media GmbH in Cologne is to manage digital city light posters (DCLP) for outdoor use in various cities in Germany. The challenge here lies in making the client’s communication message always available at the right time, in the right place...
(No credit card required)
Why Is It Important to Calculate Equipment Depreciation?
Calculating equipment depreciation is essential for financial management and budgeting. Depreciation is the decrease in the value of assets over their useful lives, and it provides a calculation to make better decisions.
It is essential for managing finance and budgeting, has implications for tax compliance, reflects the value of an asset, and provides better long-term planning. By understanding the role of depreciation in financial management and budgeting, businesses can optimize their financial performance and achieve long-term success.
What Is an Equipment Depreciation Schedule?
A typical equipment depreciation schedule includes information on assets, their initial and depreciation value, annual expense, remaining useful life, and salvage value.
Examples of schedules for different types of medical inventory equipment could range from:
- Imaging equipment such as MRI and CT scanners has a useful life of 10 to 15 years. It uses a straight line to delineate balance; its initial cost is USD 500,000. It also has a yearly depreciation expense of USD 25,000 to USD 50,000.
- Surgical equipment, such as laparoscopic instruments, has a 5 to 7 years useful life. It uses a depreciation method, such as units of production, and has an initial cost of USD 100,000, with a depreciation expense of USD 10,000 to USD 20,000.
How Do Depreciation Policies Impact Medical Practices?
Depreciation policies impact medical practices and affect financial decisions and outcomes. Moreover, depreciation policies involve determining the cost of tangible assets over their useful lives. The normal methods used are the straight-line method, declining balance method, and units of production method.
Depreciation policies impact medical practices through tax implications, capital budgeting, and accurate depreciation calculations. Medical practices align the policies with business objectives, such as improving cash flows and allocating methods for variable or consistent usage.
How Long Should Medical Equipment Last?
The average lifespan of medical equipment could last around:
- 10 to 15 years for MRI machines.
- 8 to 12 years for CT scanners.
- 5 to 10 years for ultrasound machines.
- 10 to 15 years for surgical tables.
- 5 to 8 years for cardiac monitors.
- 5 to 10 years for blood analyzers.
Factors affecting medical equipment’s longevity include regular maintenance, the intensity of usage, environmental factors, obsolescence due to technological advancements, and improper use.
Therefore, strategies to extend the life of medical equipment include creating a preventive maintenance program, training staff, implementing quality control, upgrading equipment, monitoring the equipment’s end-of-life, documenting the equipment’s lifestyle, and using third-party maintenance.
Frequently Asked Questions About the Depreciation Life of Medical Equipment
How to Calculate the Depreciation Life of Medical Equipment?
Depreciation is a crucial aspect of medical accounting. It allows businesses to recover the cost of assets over a lifetime. Here’s a step-by-step guide to calculating depreciation using different methods, examples, and tools to simplify the process. Here are a few depreciation methods.
- Straight-line depreciation focuses on the equal rate of decline in value over the asset’s useful life.
- A modified accelerated cost recovery system (MACRS) accelerates the depreciation rate in the early years.
- Units of production depreciation are calculated using equipment usage. Thus, the formula is depreciation = (cost—salvage value) x (total units produced/total units expected).
Why Is It Important to Calculate Medical Equipment Depreciation?
Recommended for you:
Book an online demo - free and without obligation - or create your free trial account directly.