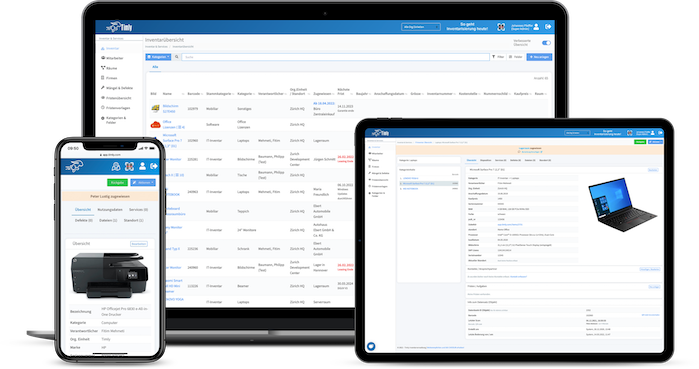
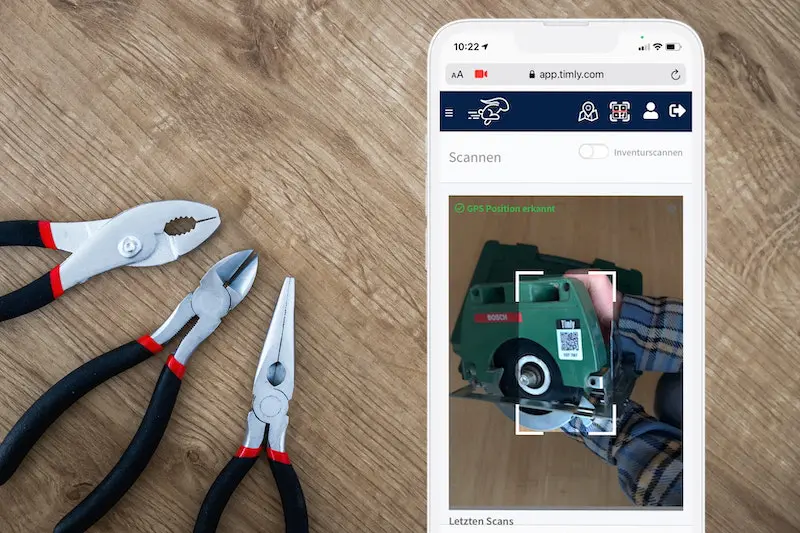
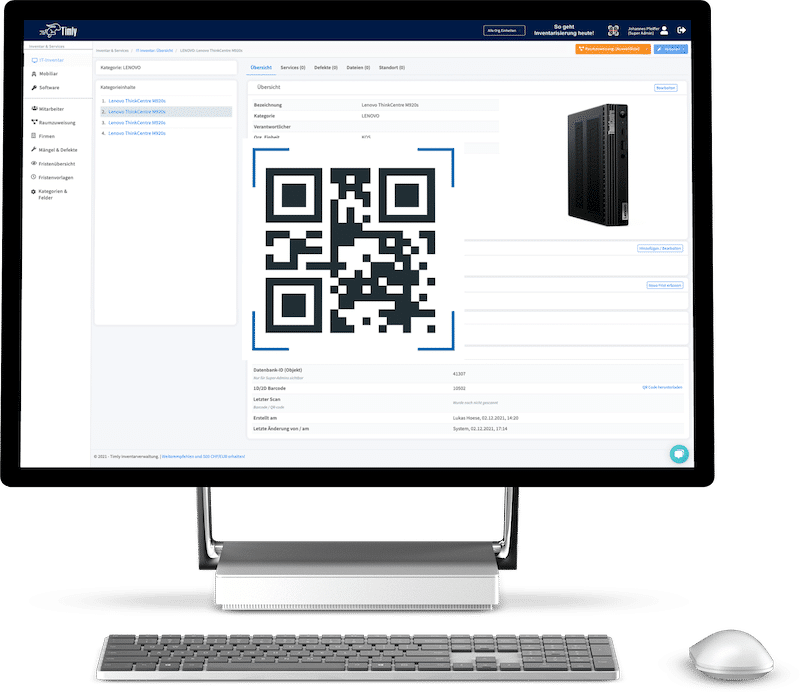
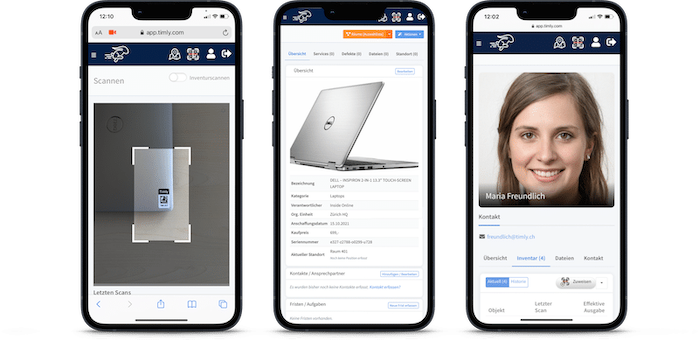
- IT lifecycle management provides a structured approach to managing IT assets from procurement to disposal, ensuring alignment with business objectives and optimizing resource utilization.
- Implementing best practices like standardization, automation, and regular audits helps mitigate security vulnerabilities, reduce downtime, and control operational costs.
- Understanding the distinct phases of planning, acquisition, maintenance, and decommissioning enables organizations to make informed decisions, extend asset lifespans, and ensure responsible disposal.
- IT Lifecycle Management
- What Are the Phases of IT Lifecycle Management?
- What Are the Best Practices for IT Lifecycle Management?
- What Is IT Asset Lifecycle Management?
- How Does the IT Infrastructure Lifecycle Work?
- Benefits of IT Lifecycle Management
- What Are the Risks of Inefficient IT Lifecycle Management?
- What Is Technology Lifecycle Management?
- What Is the Difference Between the Technology Lifecycle and the Product Lifecycle?
- What Are the Stages in Application Lifecycle Management?
- How Can IT Lifecycle Management Support Business Strategy?
- Frequently Asked Questions About IT Lifecycle Management
IT Lifecycle Management
IT lifecycle management is a method for managing the entire lifecycle of an IT asset, from its purchase to its disposal. It helps businesses align with their goals, optimize performance, reduce risks, and ensure cost efficiency throughout the asset’s lifecycle. Proper IT lifecycle management also helps boost security, reduce security risk, and prevent any form of disruption due to outdated infrastructure.
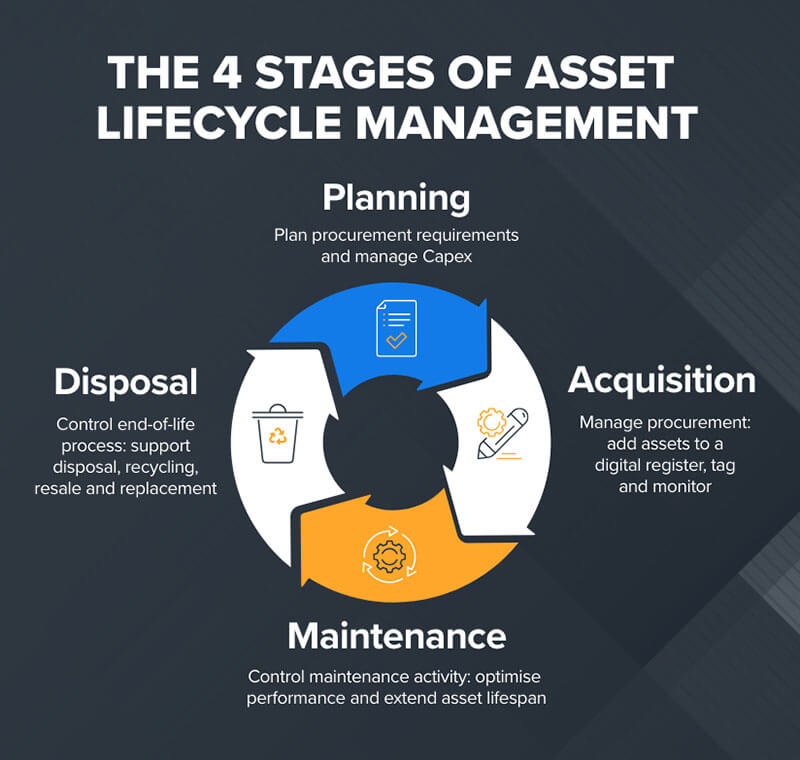
The overview of key phases in IT lifecycle management begins with planning, acquisition, maintenance, and decommissioning. The planning phase involves making strategic technological decisions to enhance current and future businesses. Thus, it is vital to consider whether the IT infrastructure at hand meets the objectives. Moreover, there needs to be ongoing support to ensure that technology is optimal and when it is time to decommission the asset, there is a proper disposal to ensure that new technology is procured.
What Are the Phases of IT Lifecycle Management?
- Planning Phase: The organization determines its business needs, sets aside a budget for the required technology, and ensures that IT goals align with business strategies. Proper IT investments are important to support the organization’s growth and objectives.
- Acquisition Phase: This phase focuses on purchasing IT assets. The vendor is selected in this phase, and assets are purchased and distributed within the organization. Therefore, ensuring that the solutions align with the business’s growth is important.
- Maintenance Phase: This phase is where assets are monitored, software is updated, and performance is optimized. This helps to ensure that the assets are always in an optimal and secure form.
- Decommissioning Phase: This phase ends the lifecycle where the IT asset is prepared for disposal. The asset data is wiped, hardware components are recycled, and inventory is updated. It helps to ensure that businesses comply with legal and environmental regulations.
What Are the Best Practices for IT Lifecycle Management?
The best practices for IT lifecycle management are:
- Standardizing IT assets is important to ensure efficiency in the organization. This is to make sure that IT assets are managed in a uniform manner and helps to reduce errors. It also can help to manage integration with other systems, which enhances performance and reduces costs.
- Automating monitoring and maintenance ensures efficient IT lifecycle management. This process tracks assets, manages patches, and reduces the rate of manual errors. Automation tools such as IT asset management (ITAM) systems can help track assets, identify issues, and address them.
Regular IT audits help identify inefficiencies and security risks. These audits also help the organization’s policies, procedures, and controls and identify vulnerabilities and threats. By constantly doing this, businesses can ensure that these threats are reduced and comply with HIPAA, GDPR, or PCI-DSS. Regular IT audits also help unearth any inefficiencies or assets not performing well with the IT infrastructure. Addressing these issues can enhance performance and security.
It is also important to consider sustainability when managing IT assets to ensure environmental responsibility. This includes disposing of old hardware, using energy-efficient equipment, and reducing electronic waste. Organizations can also consider determining strategies to enhance the lifecycle of IT assets, such as refurbishing and repurposing them.
What Is IT Asset Lifecycle Management?
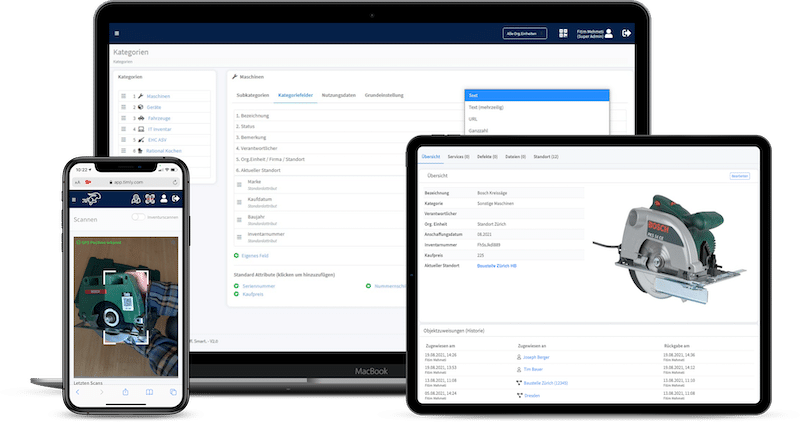
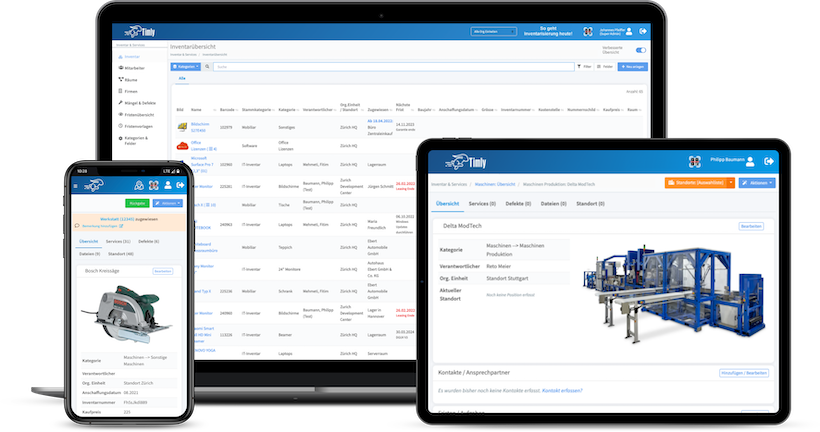
IT asset lifecycle management involves managing an IT asset management checklist from procurement to retirement. This ensures that each stage of an asset’s life is essential to meeting the business’s objectives while reducing potential risks and costs. The lifecycle has several stages: planning, procurement, deployment, usage, maintenance, and disposal.
- In the planning stage, the business will determine the need to define the potential assets that need to be purchased or updated.
- In the procurement stage, assets are purchased to provide the best value and align with the business’s goals.
- In the deployment stage, hardware and software are configured to ensure compatibility, and users are trained to ensure seamless usage.
- IT assets are monitored, maintained, and updated in the usage stage to ensure their optimization.
- In the maintenance stage, it is essential to reduce downtime and extend the lifespan of IT assets.
- The disposal stage focuses on retiring assets in an environmentally friendly manner. It requires wiping data and recycling hardware.
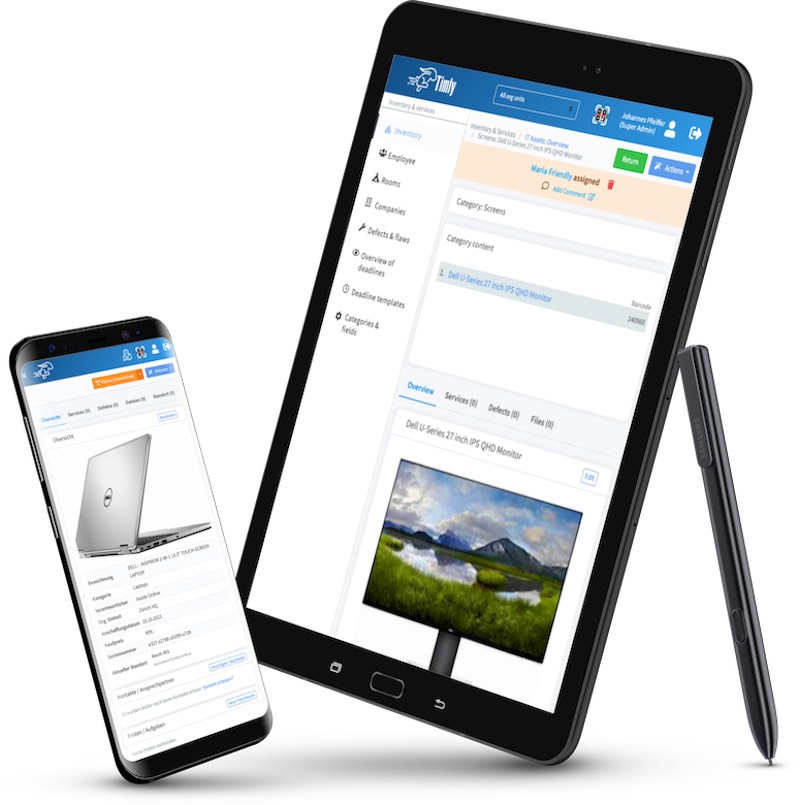
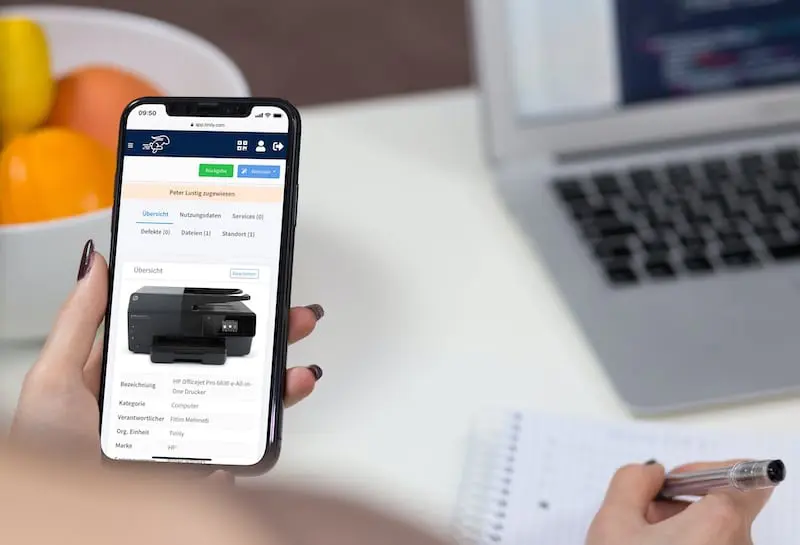
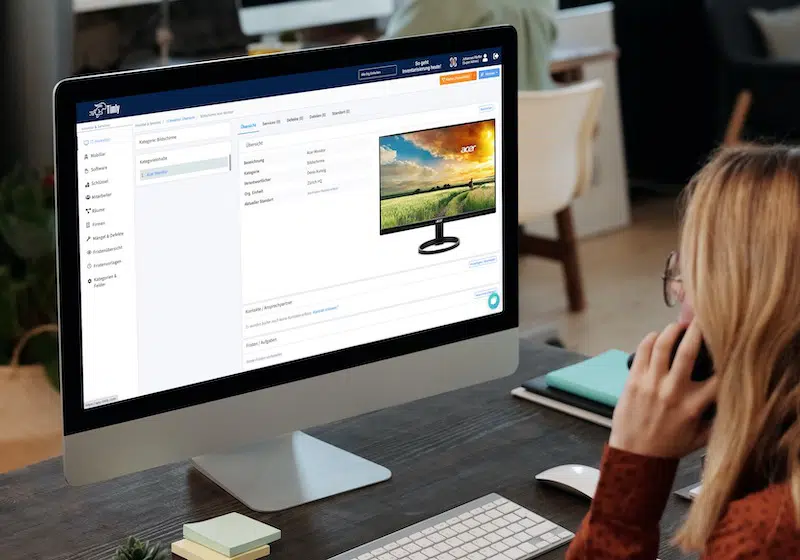
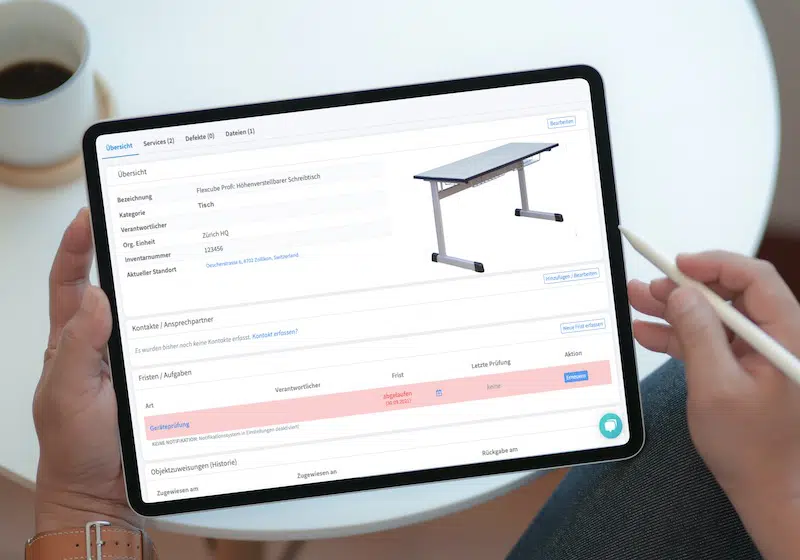
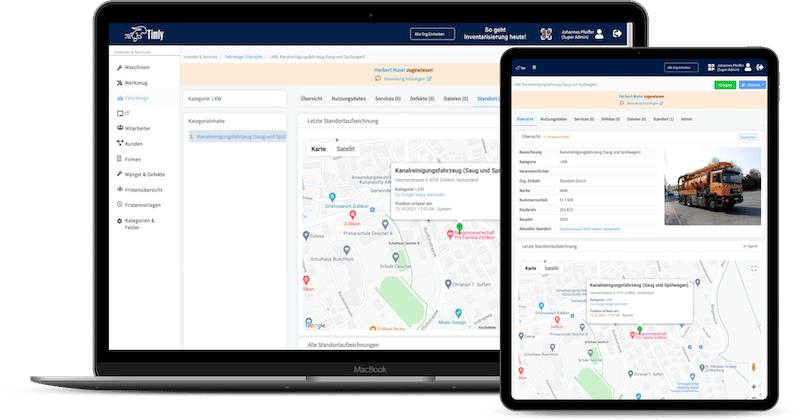
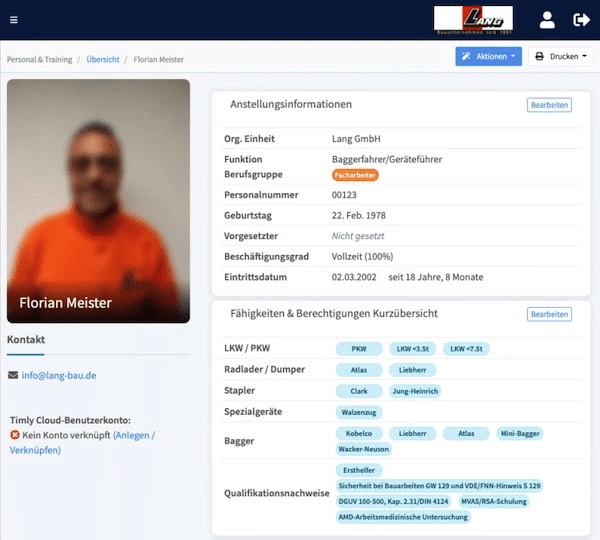
Asset tags are essential to the lifecycle management process. A digital tag is provided when an asset is purchased, ensuring the equipment is recorded, tracked, and managed throughout its lifecycle. Timly’s IT asset management software is designed to streamline IT asset management lifecycle phases. Moreover, it ensures that businesses can track, maintain, and optimize IT resources.
How Does the IT Infrastructure Lifecycle Work?
The IT infrastructure lifecycle is a systematic approach to managing the lifecycle of IT systems from procurement through retirement, ensuring smooth transitions between each phase. This structured process optimizes IT expenditures, minimizes risks, and enhances business continuity.
The lifecycle flow begins with:
- Planning and procurement are where the business determines what is needed and procures new or updated IT assets and infrastructure.
- Acquisition: This stage involves choosing IT assets, determining strategic business requirements, and determining the cost to ensure the viability of the IT systems.
- Deployment: This is where the IT sets are integrated and configured. Proper integration helps ensure that the asset provides value as soon as possible.
- Operation and Maintenance: This aids with monitoring, maintenance, and updates to ensure optimum performance.
- Retirement: This phase ensures that IT assets are disposed of safely and environmentally friendly. This stage would ensure that data is wiped, hardware is recycled, and inventory is updated.
Key metrics for success include monitoring uptime and cost-effectiveness. Uptime ensures that the IT systems always function with minimal disruptions. Efficiency ensures that the IT assets meet the business’s needs, while cost-effectiveness focuses on reducing the cost of ownership. Security is another factor important for determining potential threats. During the planning and procurement stage, choosing the right vendor and solutions for security features and compliance with industry standards is essential.

Benefits of IT Lifecycle Management
The benefits of IT lifecycle management include:
- Cost efficiency. This helps reduce expenses while optimizing IT asset procurement, deployment, and retirement.
- Risk mitigation is essential in preventing data breaches and compliance failures. By monitoring and managing IT systems, businesses can ensure that vulnerabilities are dealt with before they become threats.
- Improving IT performance involves enhancing hardware and software to align IT systems with business goals.
What Are the Risks of Inefficient IT Lifecycle Management?
The risks of inefficient IT lifecycle management are:
- Increased downtime can cause disruptions due to system failures and productivity losses. It can also affect internal operations, customer satisfaction, and overall revenue.
- Security vulnerabilities. This can cause businesses to face security threats such as financial losses and data breaches.
Moreover, inefficient ITLM can lead to higher operational costs, such as frequent system failures and downtimes. An ineffective asset management strategy can also lead to wasted budgets and more maintenance and support, thus increasing maintenance costs.
The Timly Software in Use

Optimized Device Management With Innovative Self-Inventory
SodaStream is the world market leader for water sparkling systems for domestic use and has a lot of IT equipment at its various locations. Many colleagues now work from their home offices. A digital solution for the efficient management of IT end devices became necessary...

Panasonic x Timly: Driving Technological Innovation
One of the most remarkable aspects of human ingenuity is our ability to innovate. Innovation is embedded in the DNA of consumer electronics giant Panasonic, which has diversified into a number of sectors, from heavy industry to construction...

Manage Video Equipment Efficiently Without Much Effort
The Hamburg media company always does outstanding journalistic work and is characterized by independent reporting. In order to maintain journalistic quality, the teams work with highly specialized devices – these need to be managed efficiently...

Smart City Asset Management – Timly in Use at DIGOOH
The core business of DIGOOH Media GmbH in Cologne is to manage digital city light posters (DCLP) for outdoor use in various cities in Germany. The challenge here lies in making the client’s communication message always available at the right time, in the right place...
(No credit card required)
What Is Technology Lifecycle Management?
Technology lifecycle management ensures that technological solutions are managed throughout their lifecycle, from purchase to retirement and disposal.
Here are the lifecycle stages:
- This focuses on introducing the conceptualization. It is where research and development, feasibility studies, and prototyping of the asset are conducted.
- Growth that focuses on gaining traction and market acceptance. This focuses on development and marketing efforts. The focus is to scale production and deployment.
- Maturity reaches its performance and market saturation. Efficiency improvements and cost reductions are the key focus.
- The decline phase occurs when technology becomes obsolete. When an item starts to phase out, it is time for replacement.
- The replacement phase is when it is time to decommission the technology. Ways of disposing of the data and transferring the information to the new system begin.
To implement a successful strategy, businesses must develop a detailed plan, build a strong partnership with a suitable vendor, stay current with the latest technology, and use data and analytics to make informed decisions.
What Is the Difference Between the Technology Lifecycle and the Product Lifecycle?
The difference between the technology and product lifecycle is how business and IT professionals use it. Though different, the concepts overlap because they focus on product development and enhancement.
The technology lifecycle is a broader concept that impacts several sectors. It starts with development and ends with disposal. It does not merely focus on the product but on the entire infrastructure and its evolution. Thus, understanding the technology lifecycle helps organizations manage, optimize, and plan the IT investments they are considering.
The product lifecycle focuses on the stages of assets from purchase to disposal. It includes an introduction, growth, maturity, and decline, focusing on the product’s sales, marketing, and customer satisfaction benefits. The overall idea is to ensure profitability and market share.
Both these lifecycles intersect. For instance, during the growth stage, a bus company might introduce multiple new products that leverage emerging technology. As these products mature, the business must continue to innovate and adapt to new technologies to maintain market relevance and profitability.
Here are some ways that businesses can manage both technology and product lifecycle.
- Planning: Technology should align with business objectives. The business must see that technology drives organizational success.
- Allocating Resources: This stage needs to optimize the current system, and the R&D team should start exploring new developments and technologies.
- Innovating and Retirement: Determine that businesses must innovate continuously and ensure that outdated products do not become liabilities.
What Are the Stages in Application Lifecycle Management?
The stages of application lifecycle management are:
- Planning and Development: This is when software is designed, and the goals of the application and architecture are developed to ensure that the requirements are met.
- Testing and Development: This phase focuses on testing the product, working well, and being deployed in the organizations.
- Maintenance and End-Of-Life: After deployment, support and maintenance issues are addressed. Once an application ends, it will be decommissioned and replaced with a newer one.
How Can IT Lifecycle Management Support Business Strategy?
IT lifecycle management can support business strategy by providing visibility of asset utilization and ensuring that businesses can make strategic planning and decisions with the information obtained. This visibility allows them to track and manage IT asset inventory management from when they were purchased to when they were disposed of.
IT lifecycle management provides insights into utilization, allowing organizations to optimize resources and reduce costs. To determine operational efficiency, the team can monitor a thorough inventory of IT assets, performance, and inefficiencies. Leadership can use IT lifecycle data to support business objectives. Thus, by understanding the lifecycle stages, investors and decision-makers will know when it is time for maintenance upgrades and effectively manage obsolescence.
Frequently Asked Questions About IT Lifecycle Management
What Is the Difference Between the Technology Lifecycle and the Product Lifecycle?
How Can IT Lifecycle Management Support Business Strategy?
Recommended for you:
Book an online demo - free and without obligation - or create your free trial account directly.