- Building automation maintenance involves regular inspections, repairs, and upgrades to ensure optimal performance of building systems.
- Proactive maintenance strategies, such as predictive and real-time monitoring, can significantly reduce downtime and operational costs.
- Key components of a building automation system include sensors, controllers, and actuators that work together to monitor and control building functions.
- Building Automation Maintenance
- Difference Between BAS and BMS
- Difference Between BAS and IAS
- Different Types of Building Automation Controls
- What Does a Building Automation Technician Do?
- Basic Components of a Building Automation and Control System
- Importance of Building Automation Maintenance
- Preventive Maintenance for Building Automation Systems
- Challenges of Building Automation for Larger Facilities
- What Is the Life Expectancy of a Building Automation System
- How Much Does a Building Automation System Cost?
- Frequently Asked Questions About Building Automation Maintenance
Building Automation Maintenance
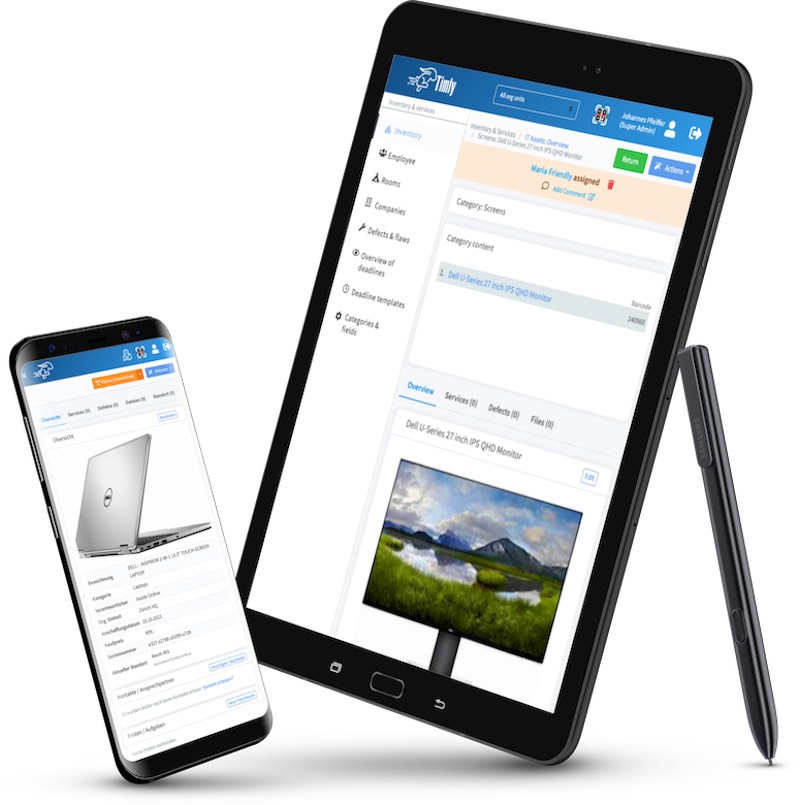
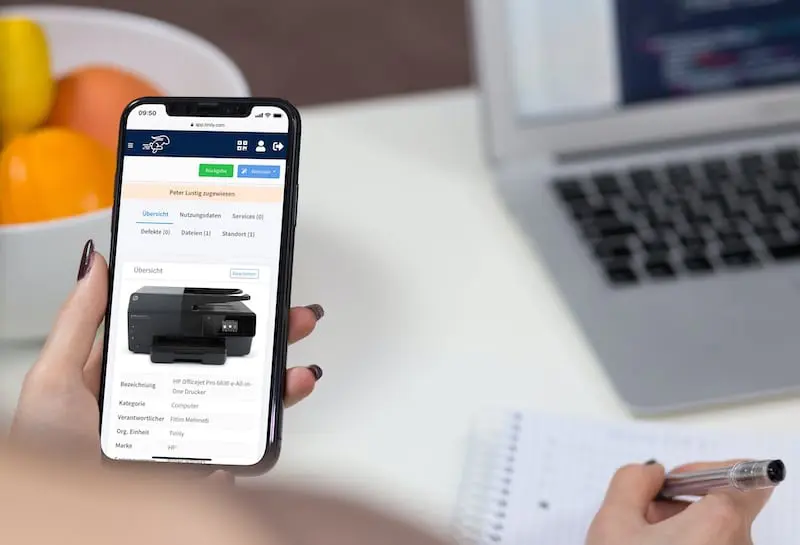
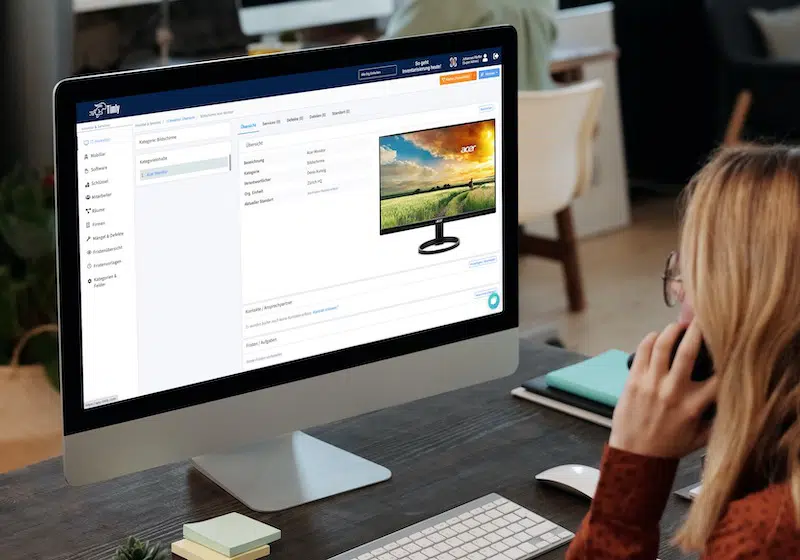
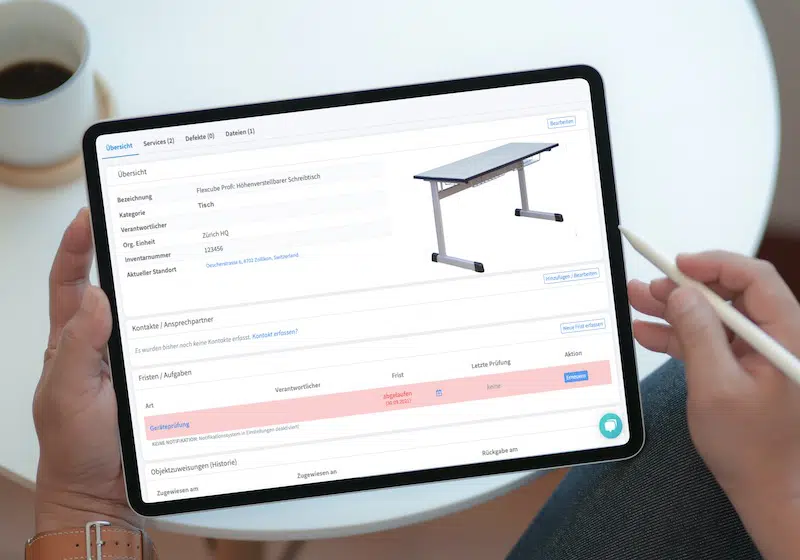
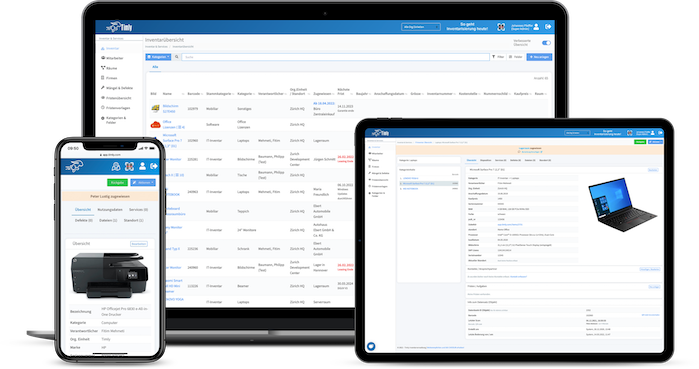
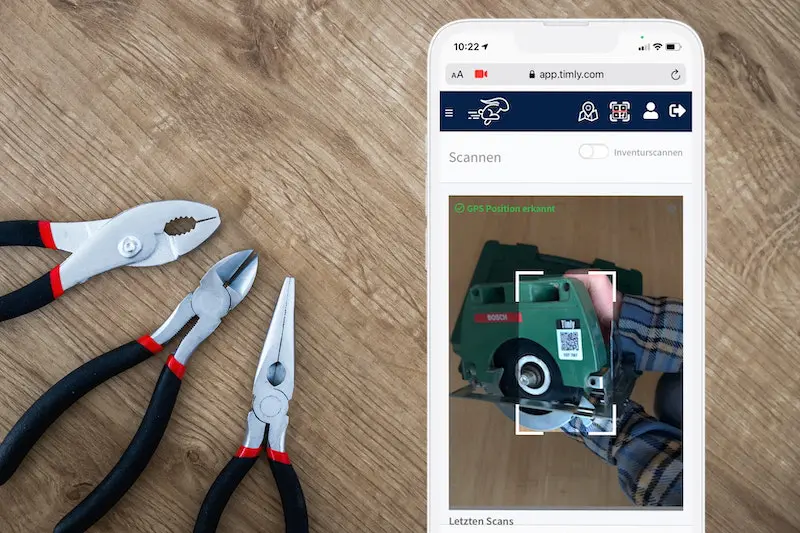
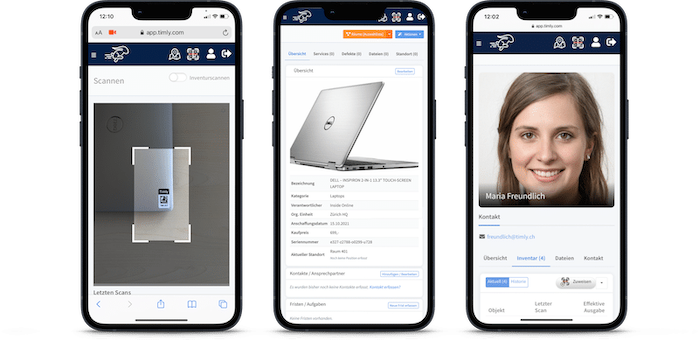
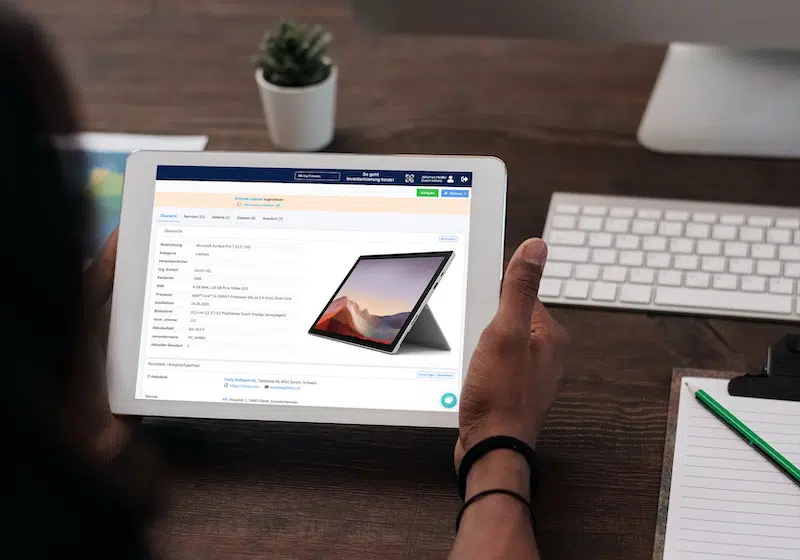
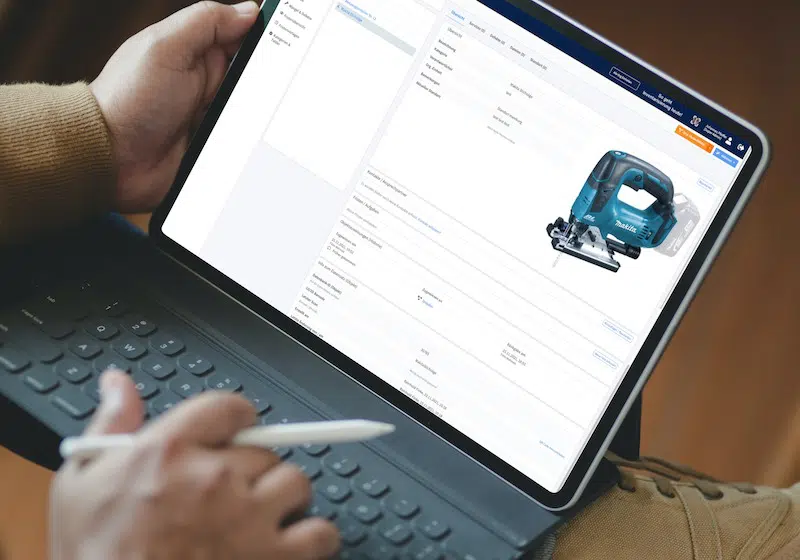
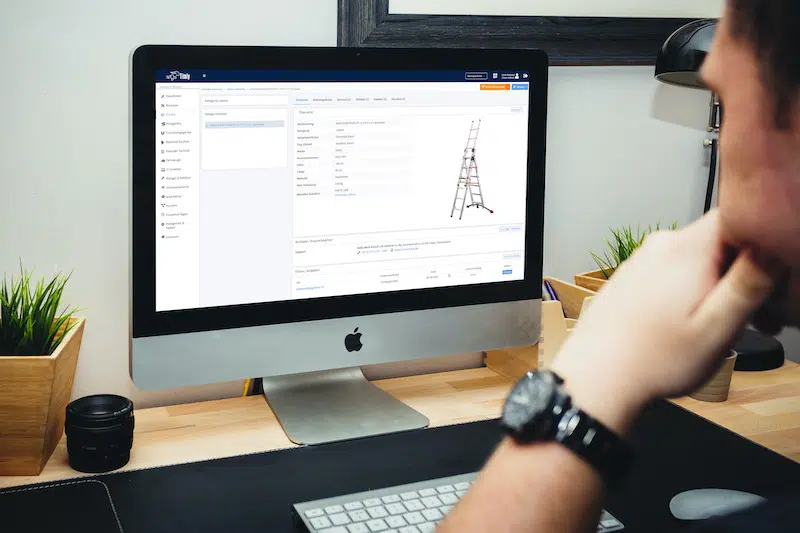
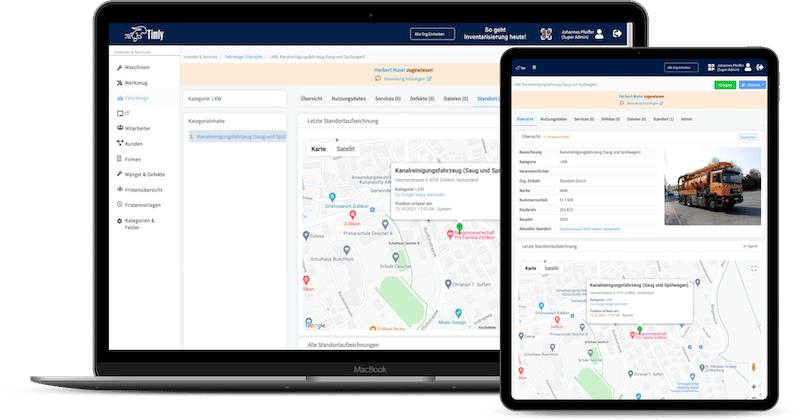
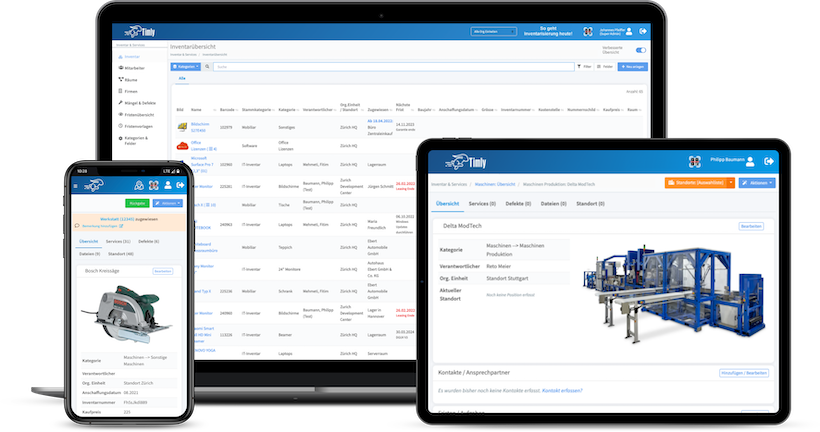
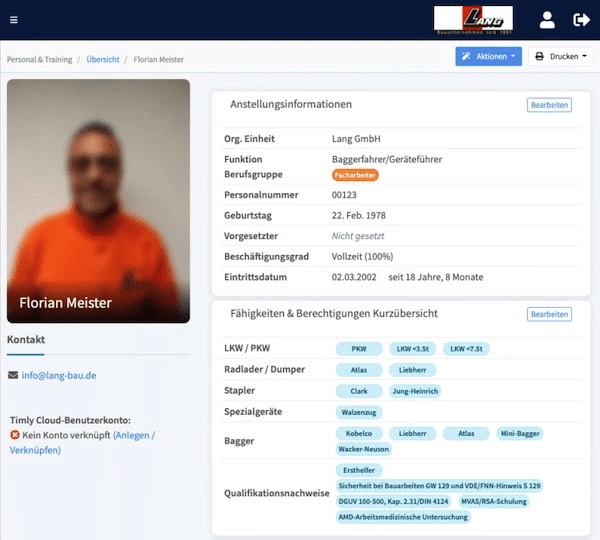
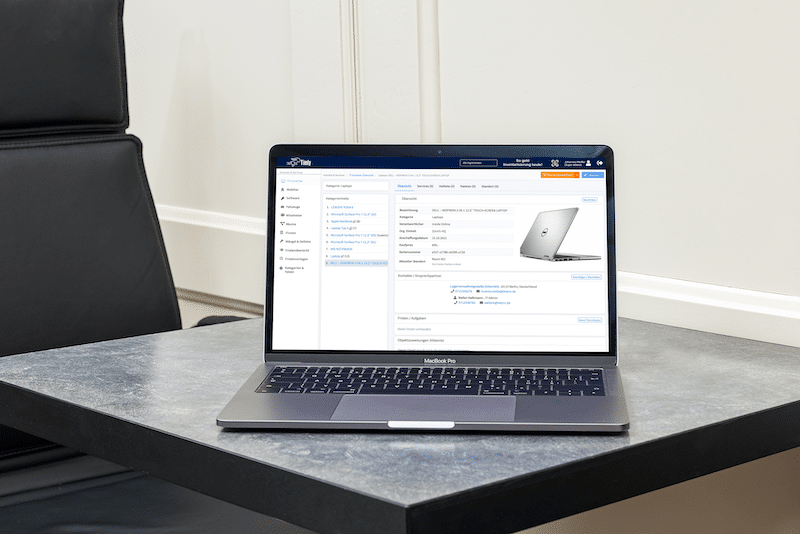
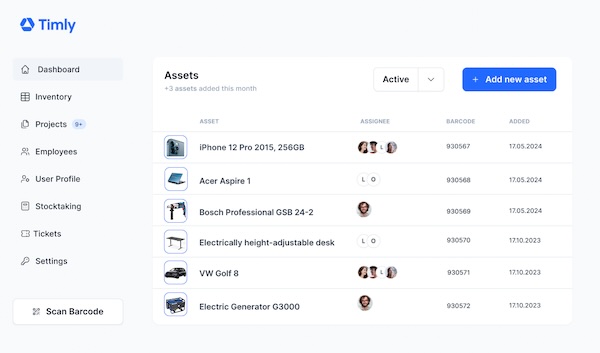
Building automation maintenance assists building equipment and facility management in managing machines, devices, fire extinguishers, elevators, HVAC systems, pumps, valves, and more. This would include tracking the last location, asset registration, and inventory management.
It also allows individuals to schedule and track maintenance so that equipment is serviced according to recommendations and regulations. Moreover, it helps manage work orders, such as assignments, notifications, task descriptions, and work status updates.
In addition, it provides inspection, and information can be retrieved to report the equipment’s production. Moreover, personnel can check for upcoming maintenance deals, detect failures and issues, and determine whether inventory is low. By integrating with IoT sensors, record-keeping, maintenance, and inspection can be performed, and equipment compliance with standards and regulations can be determined.
By utilizing Timly’s building automation maintenance, personnel can reduce downtime, extend equipment lifespans, ensure safety, improve compliance, and promote transparency in building automation maintenance.
Organizations can use building automation maintenance to reduce equipment downtime, enhance system operation, reduce costs by maintaining and managing downtime, and ensure operational efficiency.
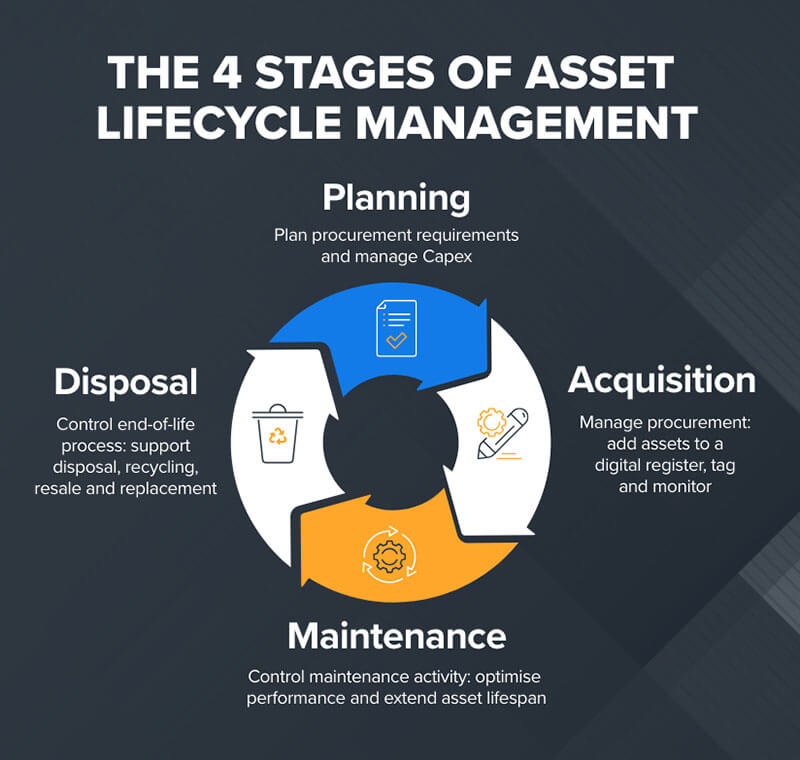
Here is the relationship between maintenance and the prolonged system lifecycle.
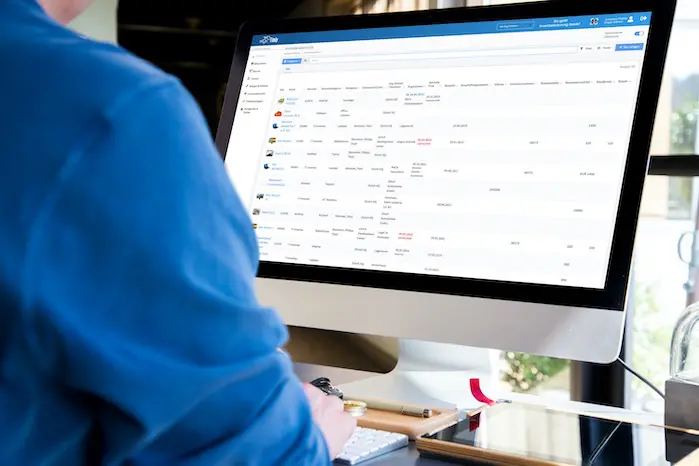
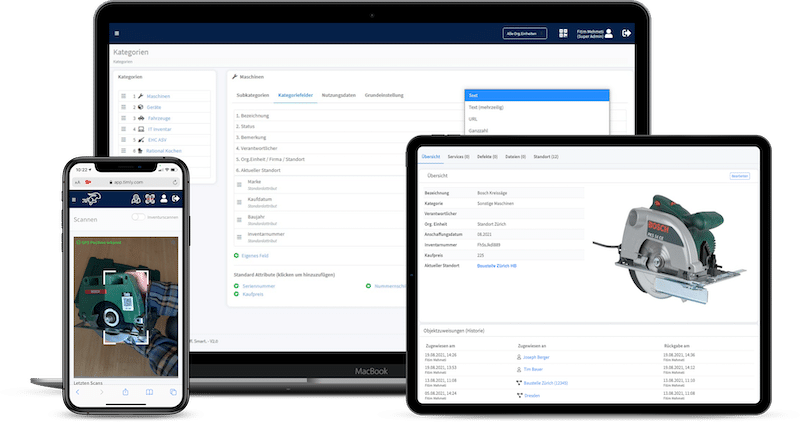
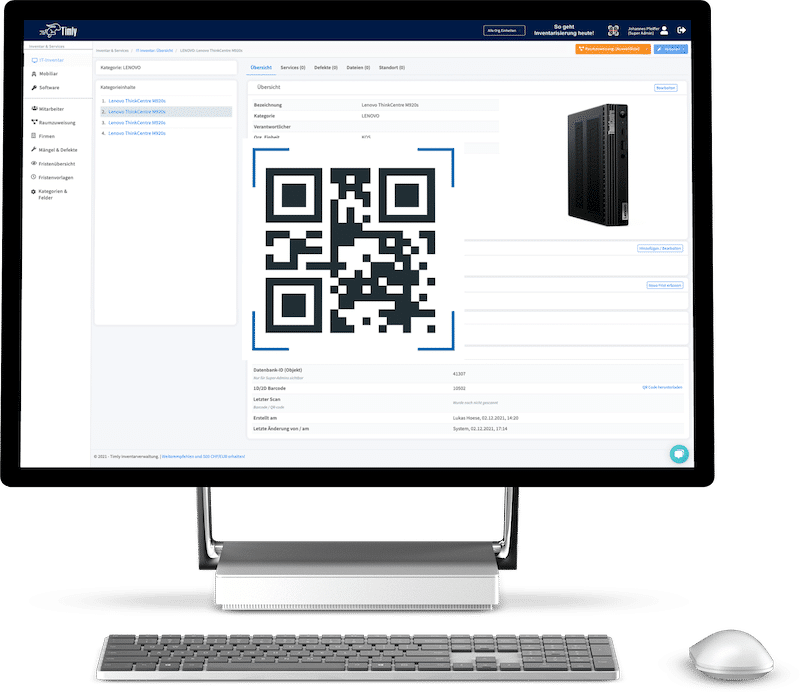
- It provides a centralized system for storing and managing assets. Users can view documentation on specifications, upcoming maintenance schedules, and previous maintenance histories.
- It allows technicians to track the progress and status of equipment.
- It enables personnel to gather data and generate reports. The team can use the information to check performance, analyze trends, and optimize strategies.
What Does a BAS Typically Consist Of?
A building automation system (BAS) normally consists of:
- IoT and predictive maintenance sensors measure information sent to the BAS.
- Controllers that process information from items such as heating, ventilation, HVAC, lighting, and many more.
- A dashboard that has interfaces that allow personnel to monitor items. This can range from web-based or mobile interfaces.
Thus, this information is utilized to help monitor various items in the building, optimize energy and reduce waste, provide information to improve productivity, enhance safety, and allow for information to be extracted and analyzed by personnel.
Some BAS systems use systems such as:
- IoT.
- Cloud-based asset management platforms.
- Artificial intelligence and machine learning.
Examples of systems that can be integrated range from HVAC and lighting controls to security systems and fire safety systems. Moreover, BAS can be integrated with systems for seamless integration to:
- Optimise performance and reduce downtime.
- Ensure that operations are optimized.
- Reduce possible human error.
- Identify issues that could be critical to maintaining costs.
Difference Between BAS and BMS
Building automation systems and building management systems are typically used interchangeably. However, they differ in functionality.
Building automation systems (BAS) focus on HVAC, lighting, security, and energy management. They mainly monitor systems and manage hardware such as sensors, actuators, and controllers, focusing on specific building systems.
BMS focuses on a broader range of services, such as HVAC, lighting, security, fire alarms, energy, waste and water management, and building surveillance. It also tracks and optimizes energy, identifies faults and issues, schedules maintenance, monitors building conditions and integrates with other third-party applications.
The difference between BAS and BMS is:
- The scope is where BAS focuses on building systems, and BMS focuses on a broad range of systems and operations.
- BAS focuses on control and automation functionalities, while BMS focuses on managing and monitoring comprehensive systems.
- BMS can integrate with many types of systems and applications, while BAS is more limited in integrating a single or a few systems.
Difference Between BAS and IAS
Building automation systems (BAS) and industrial automation systems (IAS) are automation systems that have been designed to optimize systems and equipment performance. Let us look at some key differences between BAS and IAS:
- BAS collects information on building HVAC, lighting, security, and energy management. IAS focuses on processes and assets located in multiple locations. It is generally used in the manufacturing, production, or processing industries.
- BAS focuses on managing energy, comfort levels, and maintenance. IAS, on the other hand, focuses on controlling processes, productivity, and overall quality.
- BAS focuses on automation and integrating many systems and sensors for optimization and focuses on control strategies and processes or equipment
- BAS focuses on protocols such as LON or Modbus, whereas equipment industry-standard protocols such as Profibus. Modbus,
- BAS can integrate with building systems such as fire alarms, access controls, and CCTV. IAS can integrate with other industrial features, such as manufacturing execution or enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems.
- BAS is complex, with many control, monitoring, and processing layers. Though IAS may be complex, it focuses on a single process or type of equipment.
Different Types of Building Automation Controls
Building automation focuses on using controls to manage and optimize building operations. It uses two categories: Direct Digital Controls (DDC) and Programmable Logic Controllers (PLC). Let us look at each of its applications and advantages.
DDC uses signals to control and monitor systems such as HVAC, lighting, and security, which are used in various environments. Moreover, DDCs control HVAC temperature, humidity, and air quality. They also manage lighting levels and schedules. In addition, DDS can integrate with alarm systems and monitor building events. The advantages of using a DDC system are that it is easy to install, cost-effective, supports many protocols and standards, and can be integrated with different building systems.
As for programmable logic controllers (PLCs), it uses devices with CPUs to automate industrial environments. Therefore, providing reliable information to data centers and manufacturing industries is important. It can also handle many important inputs and outputs in complex systems such as fuel systems, chillers, and boilers. The advantage of using PCL is that it is customizable and uses open-source tools to integrate with applications such as SQL and MQTT.

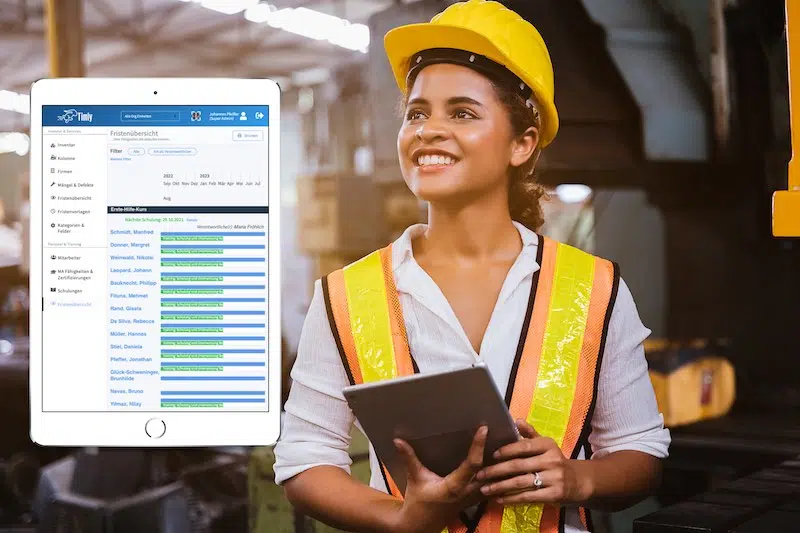
What Does a Building Automation Technician Do?
A building automation technician is responsible for:
- Monitoring the BAS so operations run smoothly and detecting any issues before they affect operations.
- Performing maintenance, repairs, and replacement of any items that have become faulty.
- Testing and modifying systems to ensure they operate at optimum levels.
- Documenting and keeping records of maintenance updates, repairs, and upgraded systems. This is to ensure compliance and regulations are up-to-date.
- Working with other personnel to ensure that systems, technical support, and troubleshooting are current.
- Extracting and analyzing information to provide a report of system implementation, optimization, downtime issues, and future risk assessments.
The role of ensuring efficient and effective operations by the technician is to:
- Prevent downtime and proactive maintenance.
- Ensure that industry standards and regulations are met.
- Determine issues that may become a problem, such as system failures and downtime.
Basic Components of a Building Automation and Control System
Let us look at the basic components of a building automation and control system.
- Sensors: BACs detect and note many parameters, such as light, humidity, temperature, and movement inside the building. These sensors send data to the controller, which allows conditions within the building to be monitored and adjusted.
- Controllers: Sensor information is sent to the actuator, which automates HVAC, ventilation, lighting, heating, and security systems.
- Actuators: This component executes the information received from the sensors and controllers.
These three components work together to ensure that building equipment functions, such as:
- Monitoring sensors, analyzing data, and executing commands.
- Monitoring data and adjusting the commands as necessary.
The Timly Software in Use

Optimized Device Management With Innovative Self-Inventory
SodaStream is the world market leader for water sparkling systems for domestic use and has a lot of IT equipment at its various locations. Many colleagues now work from their home offices. A digital solution for the efficient management of IT end devices became necessary...

Panasonic x Timly: Driving Technological Innovation
One of the most remarkable aspects of human ingenuity is our ability to innovate. Innovation is embedded in the DNA of consumer electronics giant Panasonic, which has diversified into a number of sectors, from heavy industry to construction...

Manage Video Equipment Efficiently Without Much Effort
The Hamburg media company always does outstanding journalistic work and is characterized by independent reporting. In order to maintain journalistic quality, the teams work with highly specialized devices – these need to be managed efficiently...

Smart City Asset Management – Timly in Use at DIGOOH
The core business of DIGOOH Media GmbH in Cologne is to manage digital city light posters (DCLP) for outdoor use in various cities in Germany. The challenge here lies in making the client’s communication message always available at the right time, in the right place...
(No credit card required)
Importance of Building Automation Maintenance
Building automation maintenance is important to ensure building systems are optimized for performance. By having regular maintenance of the system, it will:
- Identify issues before they become a huge problem. This helps reduce the risk of system failures.
- Reduce downtime on operations.
- Extend the lifespan of equipment. This helps reduce additional costs.
- Enhance efficiency. This reduces energy consumption and costs.
Neglecting maintenance would have consequences such as:
- Failure of equipment and unwanted costs.
- Replacement of equipment before end of life.
- Enhance energy.
- Increased system downtime.
- Increased risk of accidents and injuries.
Timly’s building automation maintenance boosts optimum operations, thus providing safety, comfort, and efficiency in reducing downtime and costs.
How Can You Reduce Downtime With Building Automation Maintenance?
To reduce downtime with building automation maintenance, it is important to employ a few strategies to reduce downtime and to ensure that operations run smoothly. Let us look at a few of these strategies.
- Scheduling maintenance that focuses on routine maintenance to check for replacements, software updates, and calibration.
- Utilizing predictive maintenance examples using IoT sensors and data analytics to predict possible downtimes.
- Using real-time monitoring alerts, dashboards, and remote access to read and analyze data for a fast response.
Maintenance reduces system destruction by reducing downtime, increasing efficiency and safety, industrial standards and compliance, and reducing overall costs.
Preventive Maintenance for Building Automation Systems
Preventive maintenance for building automation systems is important to identify and address problems that may cause system downtime or failures. This would entail checking, cleaning, and servicing systems or equipment. The role in identifying and addressing possible problems earlier would be to:
- Ensure that any issues are addressed before they become critical.
- Replace essential components or items before they break down. This reduces the potential for breakdown and enhances the equipment’s life.
Examples of preventive measures include cleaning sensors, actuators, and components, checking connections between devices, applying lubricants to parts to reduce the risk of wear and tear, and updating software and firmware to ensure compatibility.
Challenges of Building Automation for Larger Facilities
Challenges of building automation for more extensive facilities such as hospitals, universities, or commercial sites are:
- Utilizing many systems, such as HVAC, lighting, security, and fire suppression, which must be integrated and monitored. This integration would allow for seamless and optimum operations.
- Utilizing scalable systems to manage demands.
- Utilizing vast amounts of data. This would require data management and analytics to ensure proper monitoring.
To overcome these challenges, it is important to utilize technologies such as:
- Using a single system to integrate and manage many systems. This aids in a one-stop platform for monitoring and control.
- Using cloud-based BAS to ensure access from anywhere, scalability, and flexibility. This reduces the need to utilize hardware upgrades.
- Using artificial intelligence or machine learning to analyse information from many systems. To provide prejudice maintenance, optimization, and improving efficiency.
- Using modular designs for easy upgrades and replacements of components.
What Is the Life Expectancy of a Building Automation System
The life expectancy of a building automation system may last between 10 and 15 years. This is dependent on factors such as:
- Having a high usage of the system can reduce the lifespan of BAS.
- Providing regular maintenance, such as software and hardware upgrades and inspections, can reduce unwanted failures.
- Replacing obsolete devices, therefore reducing system lifespan.
- Determining if environmental factors such as extreme temperatures, humidity, and exposure to chemicals may cause physical damage affecting the BAS’s lifespan.
The average lifespan of the system is around 10 to 15 years for a proper management system, around 5 to 10 years for a heavily used system, and more than 15 years if the usage is minimal. To extend the system’s lifespan, it is essential to ensure regular maintenance, upgrade compatibility, replace necessary items, and schedule regular maintenance.
How Much Does a Building Automation System Cost?
The cost of a building automation system depends on its size and complexity. A BAS system used in large buildings can cost between USD 50,000 and USD 700,000. Complex systems can cost between USD 50 and USD 500,000. The range of costs depends on the size and complexity, number of devices, and type of automation.
The return on investment (ROI) for using BAS ranges from:
- Reducing energy consumption.
- Increasing productivity and reducing downtime.
- Providing early detection that helps to extend equipment lifespan.
- Improving building security, which reduces the risk of theft.
Frequently Asked Questions About Building Automation Maintenance
What Is a Building Automation Maintenance System?
How Can You Reduce Downtime With Building Automation Maintenance?
To reduce downtime with building automation maintenance, it is important to employ a few strategies to reduce downtime and to ensure that operations run smoothly. They are:
- Scheduled maintenance that focuses on routine maintenance to check for replacements, software updates, and calibration.
- Predictive maintenance examples using IoT sensors and data analytics to predict possible downtimes.
- Real-time monitoring uses alerts, dashboards, and remote access to read and analyze data for a fast response.
Recommended for you:
Book an online demo - free and without obligation - or create your free trial account directly.