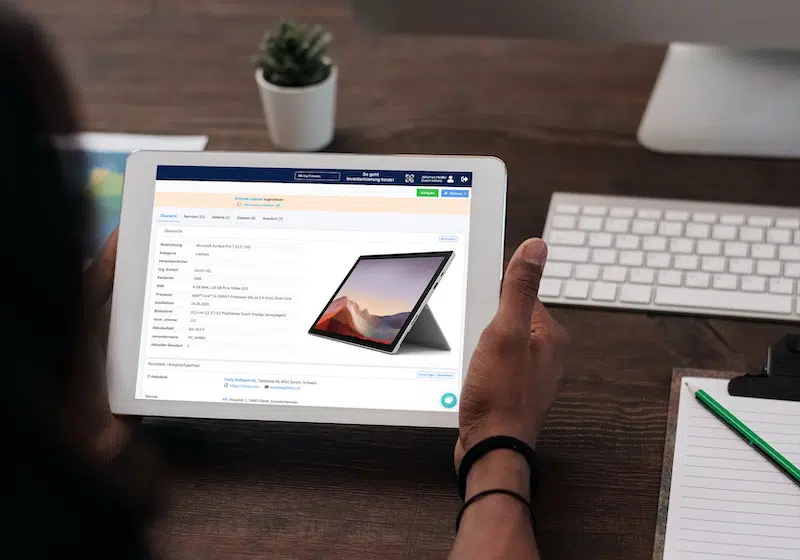
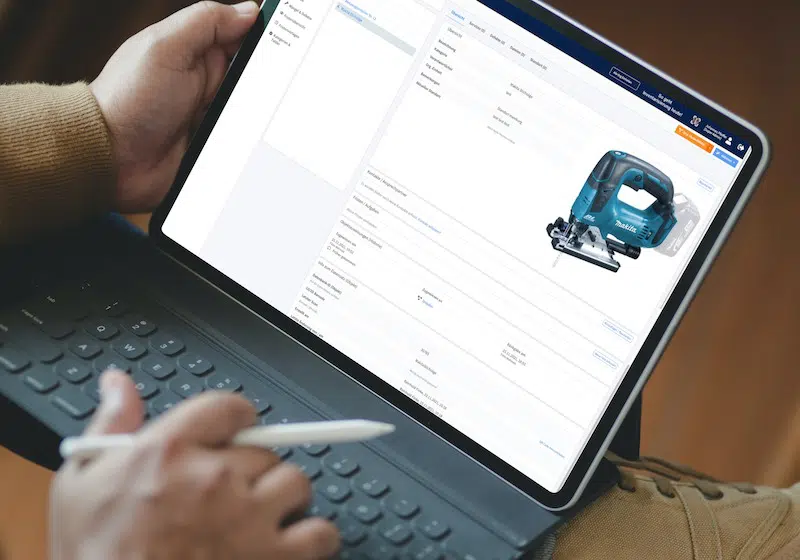
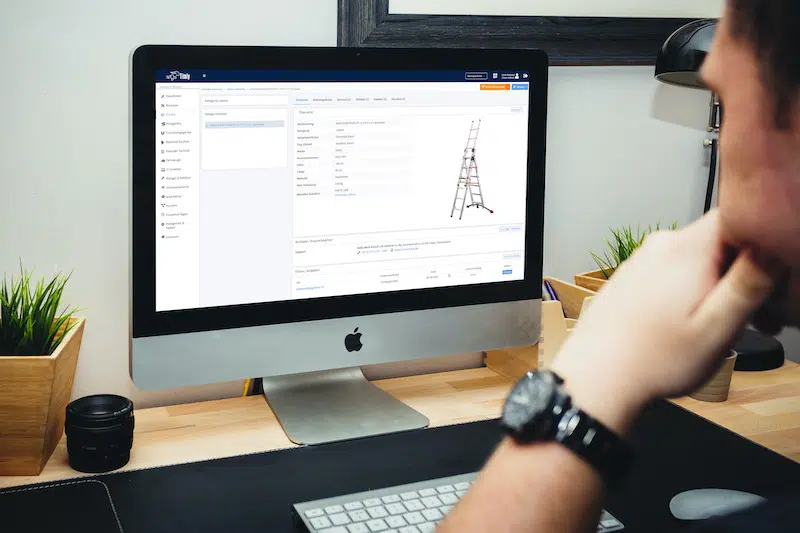
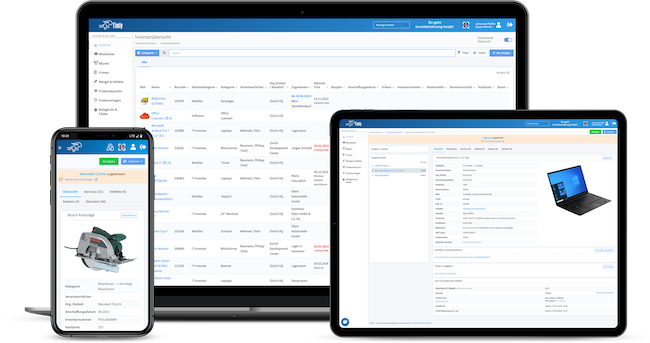
- Electrical systems are heavily regulated: These rules cover commissioning, repairs, and regular inspections to maintain safety standards.
- A structured plan ensures compliance: An electrical inspection and testing plan helps you manage tasks systematically, with all key points documented directly in the protocol.
- Digital tools streamline the process: Managing test protocols digitally simplifies inspections, secures reports, and offers practical features like automated reminders and easy access to records.
- E-Checks and Occupational Safety: Why Electrical Inspection and Testing Plans Matter
- Which Regulations Must Be Complied With?
- Inspection, Measurement, and Testing
- Key Measurements to Know in Electrical Engineering
- Who Is Authorized to Test Electrical Systems?
- Test Protocols for Electrical Engineering
- Electrical Inspection and Testing Plan: Building a Holistic System
- The Digital Maintenance Planner: Your Most Valuable Tool
- Putting Safety into Practice: Educate and Monitor
- The Right Infrastructure: The Backbone of a Digital Test Plan
- FAQs on Electrical Inspection and Testing Plans
E-Checks and Occupational Safety: Why Electrical Inspection and Testing Plans Matter
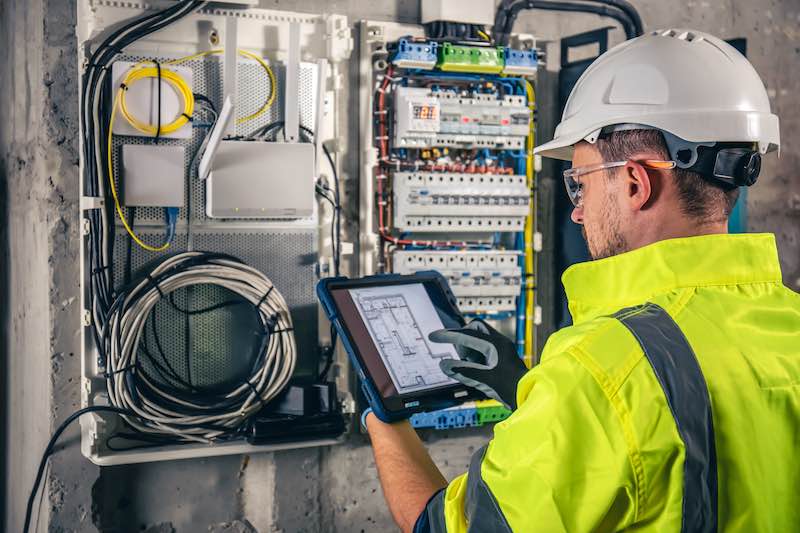
An electrical inspection schedule gives you a clear overview of all upcoming checks and deadlines. Maintaining a comprehensive electrical inspection and testing schedule is also essential for ensuring workplace safety and compliance with UK regulations.
Regular inspections, such as the Portable Appliance Testing (PAT), are mandated to verify that electrical equipment is safe for use. However, PAT is just one aspect of a broader commitment to occupational safety.
Adhering to regulations like the Electricity at Work Regulations 1989 is not only a legal obligation but also a moral one, aimed at safeguarding employees from electrical hazards. Non-compliance can result in fines and, more importantly, put the well-being of staff in danger. By creating a culture of safety and ensuring regular inspections, you can minimize the risk of accidents and promote a secure working environment.
In the UK, organizations such as the Institution of Engineering and Technology (IET) provide guidance through standards like the BS 7671 (IET Wiring Regulations). These standards form the foundation for most testing procedures, helping businesses maintain compliance and uphold safety standards.
Which Regulations Must Be Complied With?
In the UK, electrical inspection and testing are governed by several regulations designed to ensure safety and compliance across industries. Here’s a breakdown of the main ones you need to know about:
- Electricity at Work Regulations 1989 (EAWR): These regulations require that all electrical systems are maintained in a safe condition. They cover everything from fixed installations to portable appliances and apply to employers, employees, and the self-employed.
- BS 7671 (IET Wiring Regulations): This is the UK standard for the design, installation, and maintenance of electrical systems. It provides detailed guidance on safe electrical installations and forms the basis for inspections and testing.
- Health and Safety at Work etc. Act 1974 (HSWA): This act outlines the general duty of employers to ensure the health, safety, and welfare of their employees, including protection against electrical hazards.
- Provision and Use of Work Equipment Regulations 1998 (PUWER): PUWER requires that work equipment is suitable for its intended purpose and maintained in a safe condition. This includes regular inspection and testing of electrical equipment.
- Management of Health and Safety at Work Regulations 1999: These regulations require employers to conduct risk assessments, including those related to electrical systems, and implement measures to mitigate identified risks.
- Electricity Safety, Quality, and Continuity Regulations 2002 (ESQCR): These regulations apply to electrical network operators and set out requirements for the safe supply of electricity, including the inspection of fixed installations.
- Product Safety Regulations: These regulations cover product safety standards, such as CE or UKCA markings, ensuring that electrical equipment meets the required safety levels.
Simplifying Compliance
With so many regulations to follow, staying compliant can be a headache. Using templates to track the necessary attributes for each piece of equipment can help. Digital solutions simplify this further by allowing you to store and manage inspection data efficiently, ensuring that all required checks are easily accessible and up to date.
Inspection, Measurement, and Testing
Visual Inspection
Measurements
The technical aspects of testing involve specific measurements such as:
- Insulation Resistance: Ensures the system is adequately insulated to prevent leakage currents.
- Earth Continuity: Confirms that protective conductors are intact and properly connected.
- Polarity and Fault Loop Impedance: Verifies correct connections and safety of protective devices.
Functional Testing
Inspectors may also conduct practical tests to confirm that safety measures, such as circuit breakers and RCDs, operate correctly. Additional checks might include identifying unusual noise or emissions that could signal safety concerns.
Key Measurements to Know in Electrical Engineering
Accurate measurements are critical in electrical inspection and testing to ensure systems remain safe and compliant.
Requirements for Test Equipment
In the UK, all test devices must meet high standards of reliability and safety. They should comply with relevant standards like BS EN 61557 for electrical safety test equipment. Regular calibration is essential to maintain accuracy, and detailed documentation of each device’s calibration history should be kept.
Inspection intervals for work equipment vary based on its use and environment. For example, on construction sites, inspections might be required every three months, whereas in less demanding environments, intervals of up to two years could be acceptable.
Common Electrical Measurements
- Protective Conductor Resistance: This test checks the integrity of the protective conductor, ensuring it can safely carry fault currents to earth in case of an issue.
- Insulation Resistance: This measures how well an electrical system is insulated, preventing unwanted current leakage and ensuring the system is safe to operate.
- Contact Current: This test measures any current that might flow through a person when they come into contact with the equipment. It ensures that any such current is minimal and within safe limits.
In the UK, only qualified professionals are permitted to carry out electrical testing. According to the Electricity at Work Regulations 1989, individuals performing these tasks must have the necessary technical knowledge, experience, and training.
Qualifications and Certifications
Typically, this means a competent person who has:
- Completed relevant training, such as the City & Guilds 2391-52 qualification for inspection and testing.
- In-depth understanding of standards like BS 7671 (IET Wiring Regulations) and how to apply them in practice.
- Experience in performing tests and interpreting results correctly.
Company-Specific Knowledge
Beyond technical expertise, the electrician must be familiar with the specific processes and equipment within your business. This knowledge allows them to identify potential hazards unique to the workplace and tailor their testing approach to the specific equipment and environment of your work.
Proper training and certification ensure that inspections are carried out to a high standard, keeping both employees and systems safe from electrical risks.
Test Protocols for Electrical Engineering
Accurate and thorough documentation is an essential part of occupational health and safety, especially when it comes to electrical inspection and testing.
The process starts with verifying the qualifications of the person performing the tests. Equally important is ensuring that the test equipment is functioning correctly. Without this, the results could be unreliable, compromising safety.
What Should Be Documented?
For each test, the following details must be recorded:
- The object being tested (e.g., equipment or system)
- The type of measurement performed (e.g., insulation resistance or earth continuity)
- The results of the measurement
- The identity of the tester
This creates a clear, verifiable record that tracks every step of the testing process.
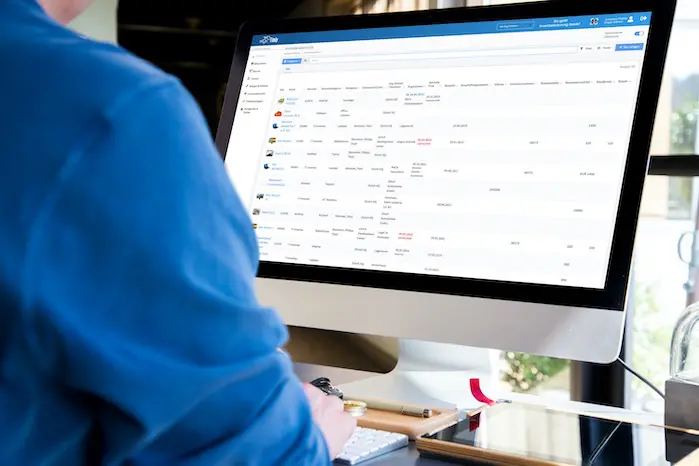
Benefits of Digital Record-Keeping
Using digital tools to manage test protocols simplifies the documentation process and makes access to records easier. On-site entries can be made in real-time, and records are securely stored, reducing the risks of lost or damaged paperwork. Digital records also ensure that information remains legible and easy to access for future reference.
In the UK, organizations like the IET and HSE provide templates and guidance for maintaining accurate electrical test reports. Switching to digital systems ensures compliance and helps businesses stay organized and efficient.

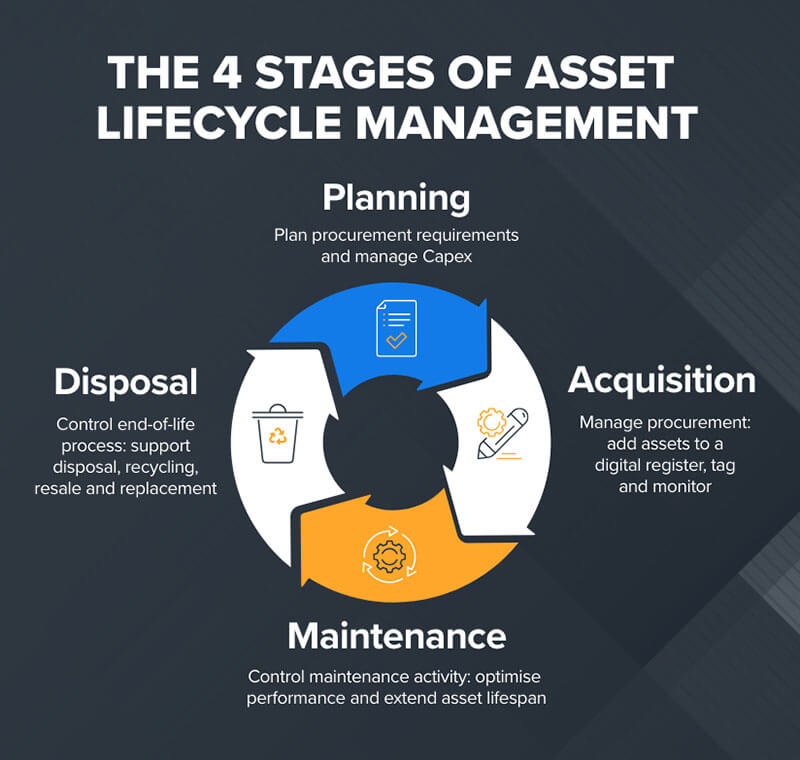
Electrical Inspection and Testing Plan: Building a Holistic System
An effective electrical inspection and testing plan lays the groundwork for a logical, efficient testing sequence. Once the plan is in place, adding new devices becomes a straightforward process.
Key Steps in Creating a Test Plan
- Define Key Dates: Start by scheduling inspection and testing dates based on regulatory requirements and company needs.
- Assign Dates to Equipment Types: Next, link these dates to specific equipment types.
It’s important to map out dependencies between equipment. Sometimes, these are simple such as devices in the same area can be tested on the same day. But in complex environments, like logistics or distributed IT systems, dependencies can span different locations. If one piece of equipment fails, it could impact an entire chain of operations. Testing plans should take these scenarios into consideration.
The Role of Digital Tools
Using software to manage your test plan ensures that no detail is overlooked. A comprehensive system should:
- Record All Assets and Equipment: Every item, from machinery to IT systems, should be logged.
- Link Items to Locations or Other Assets: This helps streamline inspections by grouping related equipment.
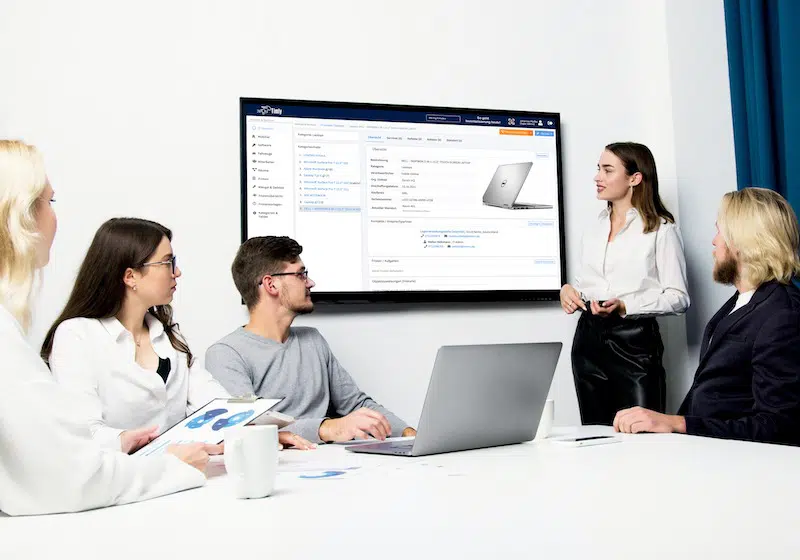
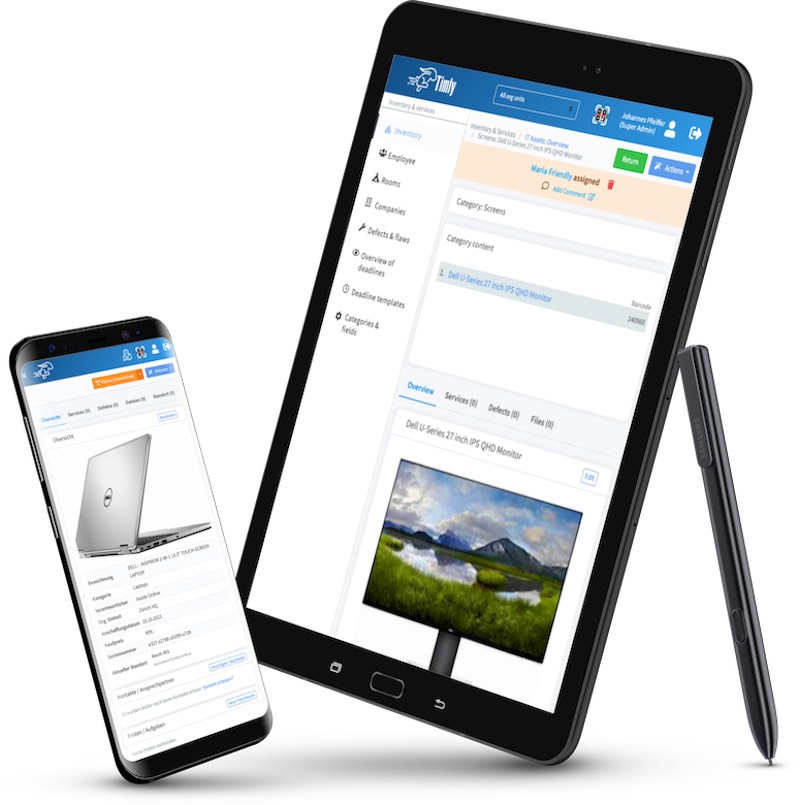
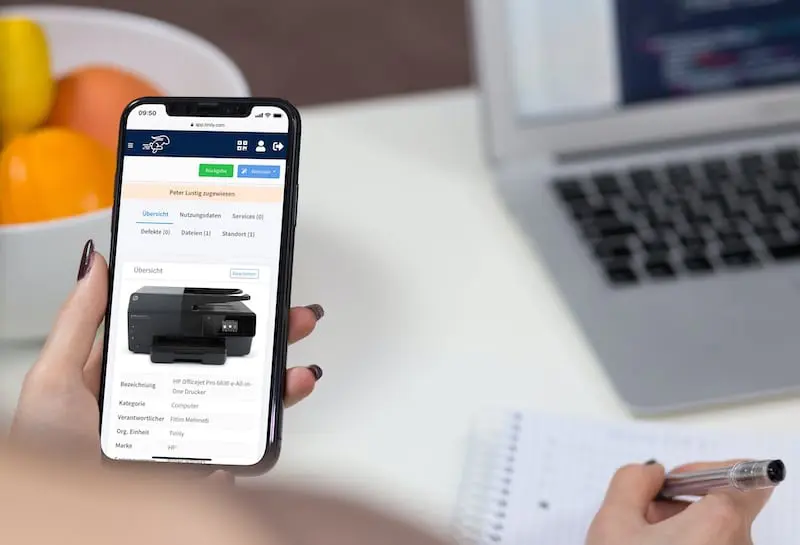
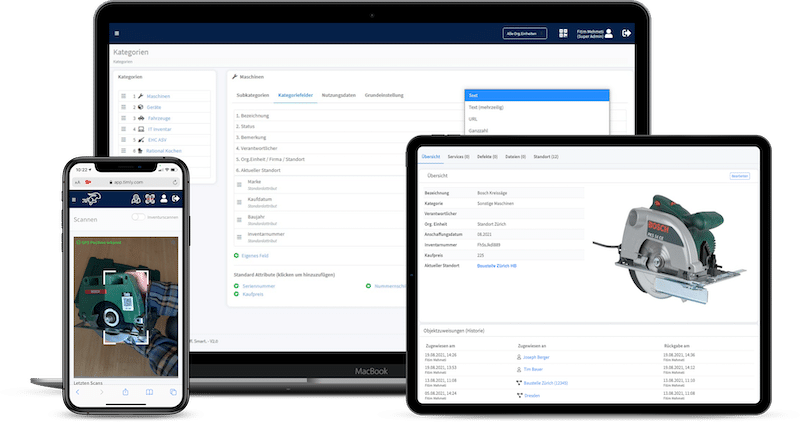
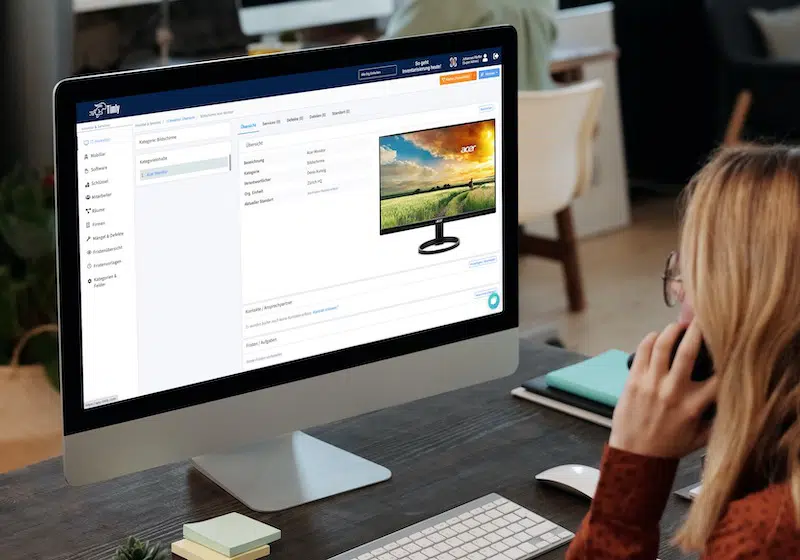
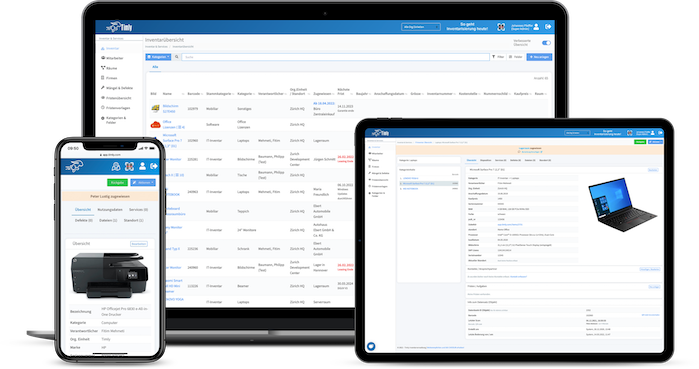
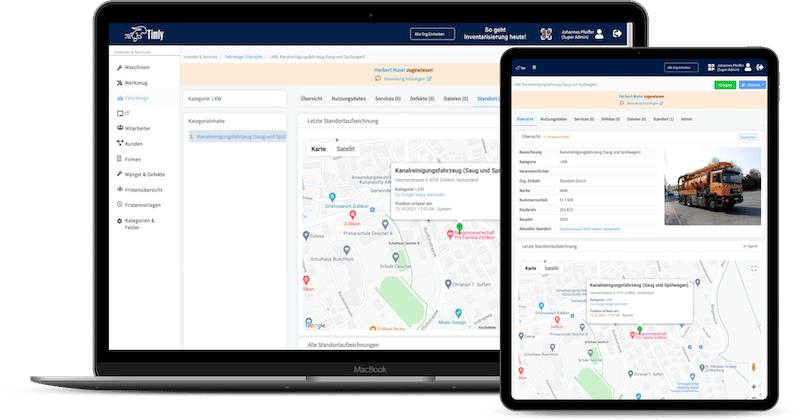
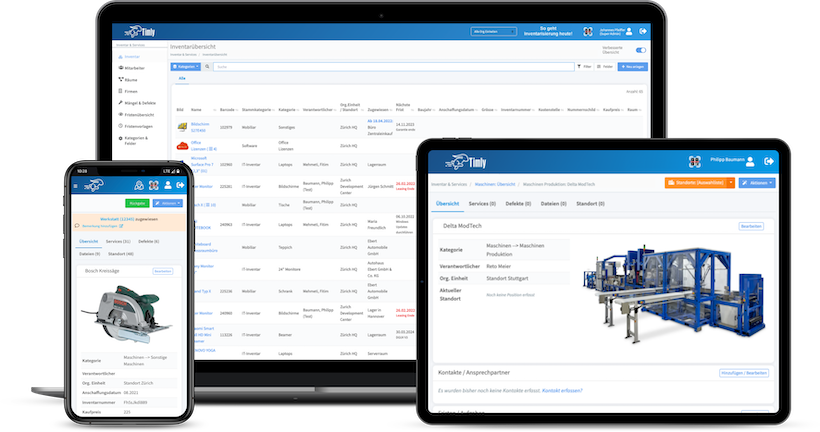
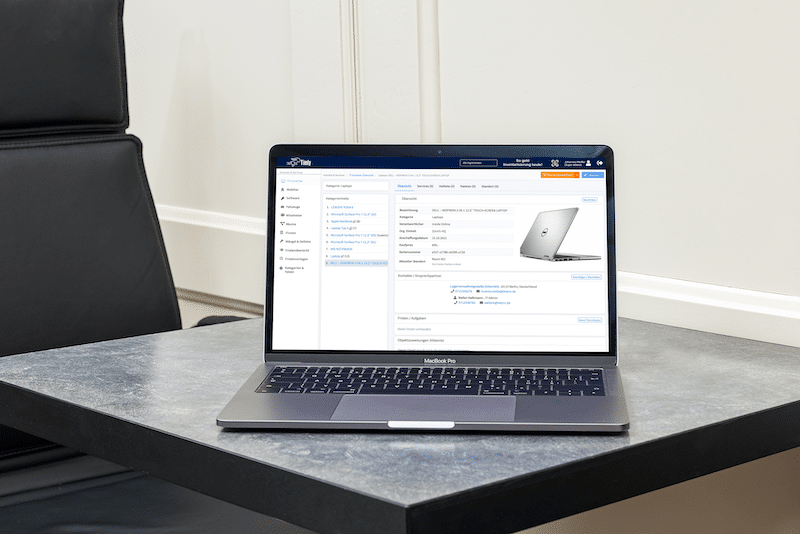
Timly’s inventory software excels in this area. It allows businesses to define “container objects” such as rooms or production areas, creating a structured approach to testing. With built-in templates, you can standardize attributes for each type of equipment, ensuring consistency across your inventory.
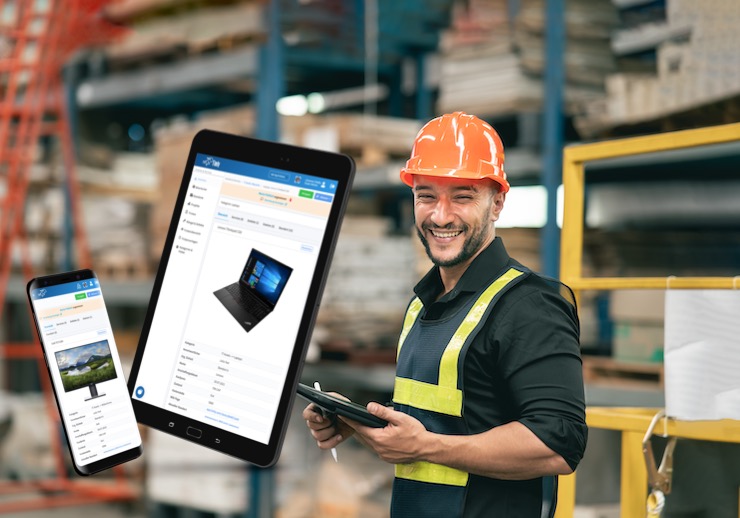
The Timly Software in Use

Optimized Device Management With Innovative Self-Inventory
SodaStream is the world market leader for water sparkling systems for domestic use and has a lot of IT equipment at its various locations. Many colleagues now work from their home offices. A digital solution for the efficient management of IT end devices became necessary...

Panasonic x Timly: Driving Technological Innovation
One of the most remarkable aspects of human ingenuity is our ability to innovate. Innovation is embedded in the DNA of consumer electronics giant Panasonic, which has diversified into a number of sectors, from heavy industry to construction...

Manage Video Equipment Efficiently Without Much Effort
The Hamburg media company always does outstanding journalistic work and is characterized by independent reporting. In order to maintain journalistic quality, the teams work with highly specialized devices – these need to be managed efficiently...

Smart City Asset Management – Timly in Use at DIGOOH
The core business of DIGOOH Media GmbH in Cologne is to manage digital city light posters (DCLP) for outdoor use in various cities in Germany. The challenge here lies in making the client’s communication message always available at the right time, in the right place...
(No credit card required)
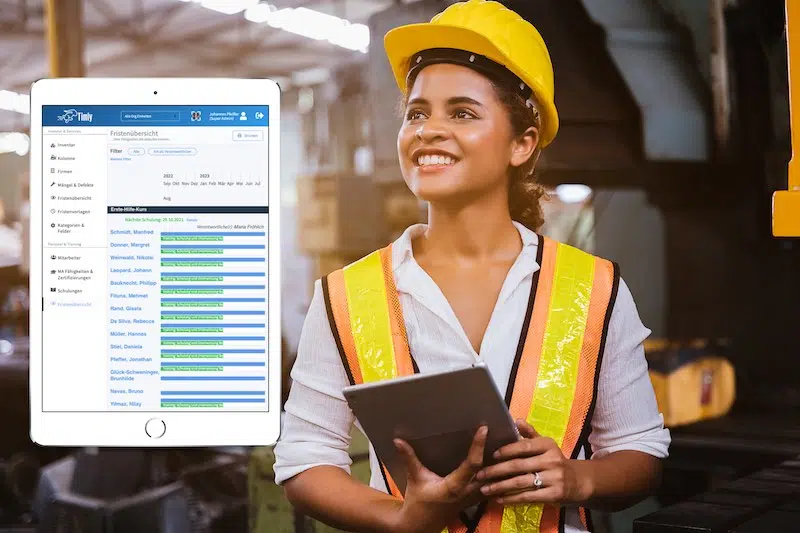
The Digital Maintenance Planner: Your Most Valuable Tool
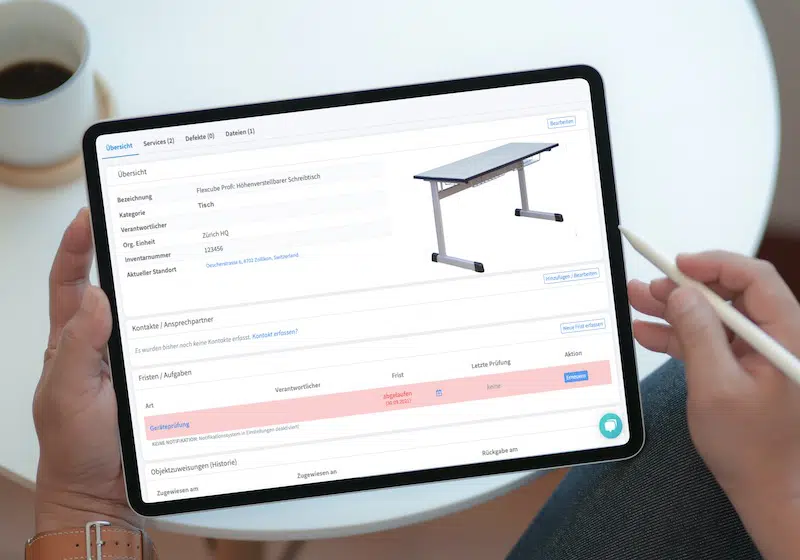
A digital maintenance planner can transform your electrical inspection and testing strategy. Each asset in your system, whether it’s a single device or a complex machine made up of multiple components, gets its own calendar. This ensures that nothing is left out, and every inspection or test is scheduled and tracked.
Flexible Scheduling and Filtering
With a database-driven system, you can filter and organize your maintenance tasks in ways that suit your business. Here are a few ways to customize your scheduling:
- By Asset Type: Group similar devices for streamlined testing.
- By Specific Test Requirements: Focus on equipment with unique inspection needs.
- By Due Dates: Prioritize inspections that are coming up soon.
- By Location: Consolidate tests for all equipment in a single area.
This flexibility allows you to create a maintenance plan tailored to your operational needs.
Stay Ahead with Automated Reminders
Modern maintenance planners, like Timly, include automated reminders. These notifications ensure that internal teams and external service providers are alerted well before deadlines. With this system in place, the risk of missing critical inspection dates is virtually eliminated.
Putting Safety into Practice: Educate and Monitor
Occupational safety hinges on two key pillars: education and control.
Informing and Training Employees
The process starts with a thorough risk assessment, followed by clear, actionable safety instructions. New employees must be trained on these procedures, and regular refresher sessions help keep safety top of mind. Building a culture of safety ensures everyone understands their role in maintaining a safe workplace.
Monitoring and Daily Checks
Safety doesn’t stop at formal inspections. Daily checks, like inspecting equipment at the start of a shift, are also an important step to prevent issues before they become more serious.
Leveraging Digital Tools for Safety
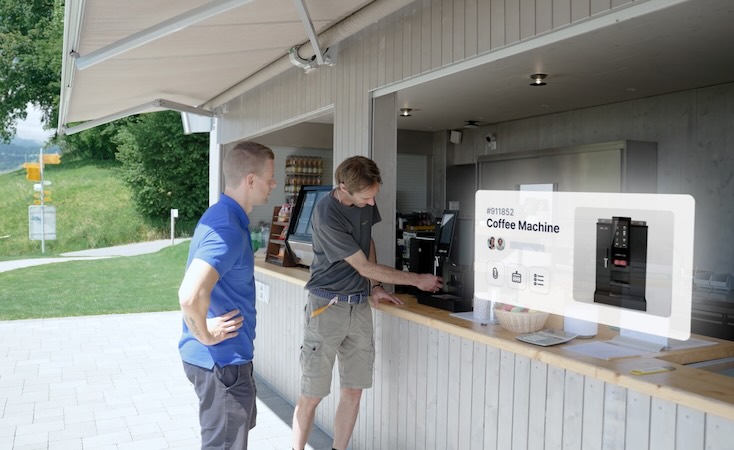
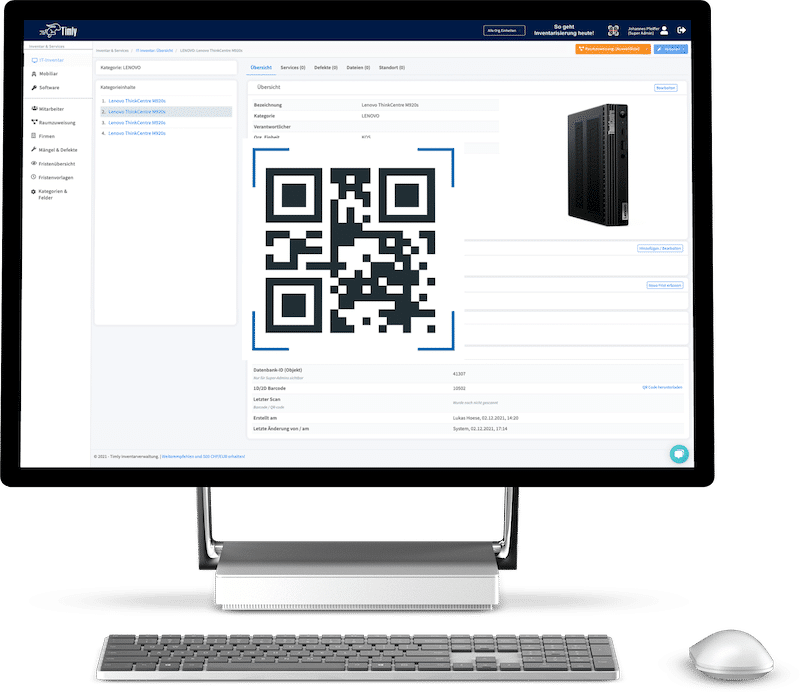
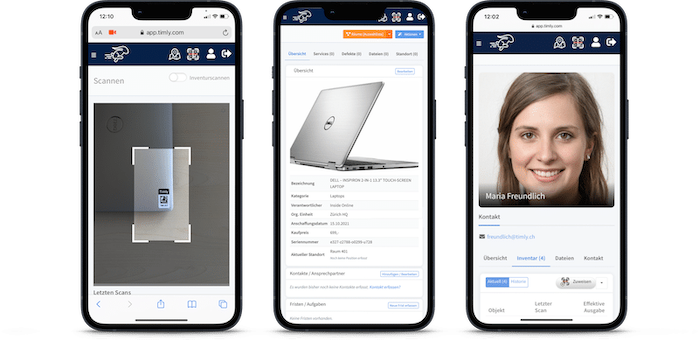
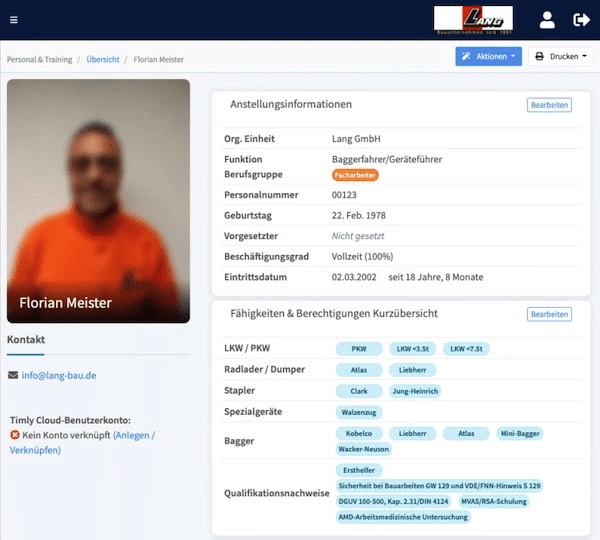
A digital approach makes implementing these measures simpler. Using inventory software, each piece of equipment gets a digital device file. You can store safety instructions, checklists, and forms directly in the device profile. Once checks are completed, they’re immediately saved to the system, giving employees an easy way to verify their equipment’s condition.
This not only keeps everyone informed but also provides managers with real-time oversight to ensure all necessary checks are carried out.
The Right Infrastructure: The Backbone of a Digital Test Plan
Cloud-Based Convenience
Timly operates as a Software as a Service (SaaS) solution, hosted on a secure cloud server. This means you don’t need complicated setups or constant access to a company network. All you need is an internet-enabled device.
Easy Access Anywhere
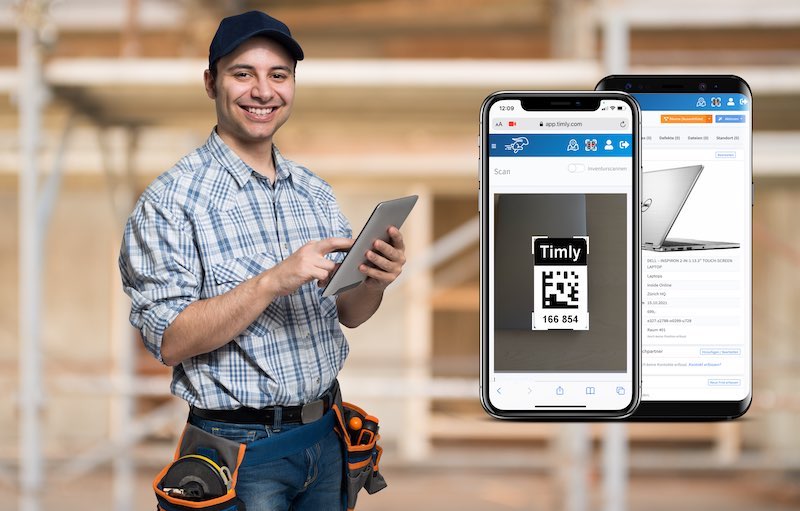
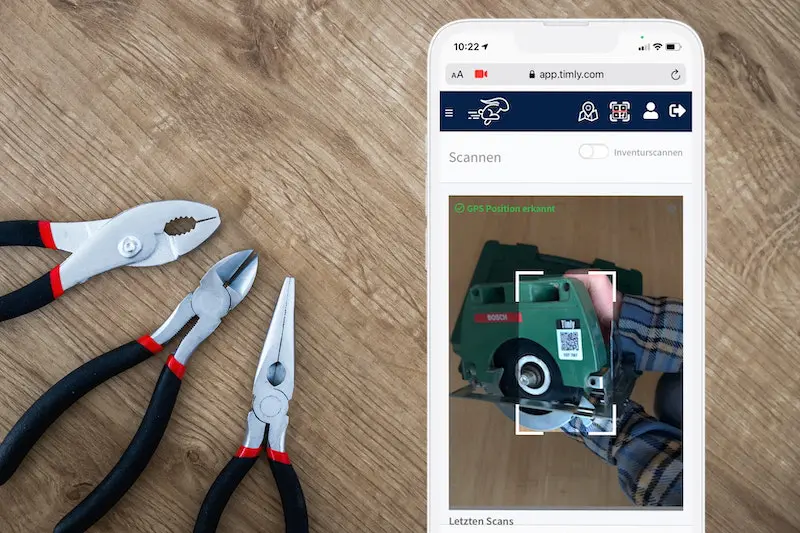
With Timly’s web app, users can log in from smartphones, tablets, or computers, accessing the database based on their level of authorisation. The platform simplifies asset management with QR codes and barcode scanning, enabling employees to quickly pull up a device’s digital profile.
Real-Time Documentation
The system allows employees to check inspection histories and perform on-the-spot inspections, with results saved directly to the cloud. This ensures that critical information is always up-to-date and accessible, even outside the company network.
By using cloud-based tools, businesses can streamline their inspection workflows while providing employees with the flexibility to manage tasks directly at the workplace.
FAQs on Electrical Inspection and Testing Plans
Why Do Companies Need an Electrical Inspection and Testing Plan?
Does Digitizing Electrical Tests Make Sense?
Absolutely. Digital maintenance calendars offer automated reminders for upcoming inspections, ensuring nothing is overlooked.
Which Software Is Best for Managing an Electrical Inspection Plan?
What Should I Consider When Choosing Software?
Recommended for you:
Book an online demo - free and without obligation - or create your free trial account directly.